Introduction
In this post, we go through the process of developing a React admin panel using Refine and daisyUI.
Refineis a React-based framework that helps quickly build data-heavy applications like dashboards, admin panels and storefronts. It comes with a headless core package that integrates with any UI framework and design system.
daisyUI is a component templates library built on top of TailwindCSS. It provides us with short semantic classes composed from TailwindCSS utilities and a growing collection of convenient component templates that helps quickly build React components for our app.
daisyUI can easily be integrated with Refine, and in this post we are going to see how to do that while building a dashboard and admin panel app using Refine's Fine Foods API.
Overview
The React admin panel we are going to build uses the Refine hosted Fine Foods API to display a dashboard of KPI data, and CRUD pages for products and categories resources. The dashboard will present various data in cards, charts and a table. And the products and categories resources will have list, create, show and edit pages.
We start this post with a brief discussion on Refine architecture - particularly how it works under the hood with React contexts backed by providers, hooks and components. We also talk about daisyUI, the short, semantic classes such as btn, menu, tab, etc., and their variants it provides and how they facilitate rapid building of React components using a growing library of prestyled daisyUI templates.
We then initialize a Refine app, and integrate and configure daisyUI. Afterwards, we move on to building the features of the admin panel.
We first build the dashboard page where we present stats for relevant KPIs in cards, charts and a table. We use the React-based Recharts library for plotting our data.
In the later half of the post, we add CRUD pages for products and categories resources. We define the resources prop on <Refine /> component, resource action paths, and their route definitions. CRUD actions covered for both resources are list, create, show, update and delete. We then make use of Refine hooks such as useTable() and useForm() for entering, fetching and presenting data from the API. We build the UI with predefined daisyUI templates for buttons, menus, tabs, stats, etc.
Towards the end, we see how to customize the layout of a Refine app. We replace the default leftside navigation to adopt a top navbar by leveraging useMenu(), useNavigation() and useBreadcrumb() hooks.
What is Refine?
Refine is a powerful React framework for building Enterprise web applications. It is particularly focused on creating data-heavy apps like dashboards, admin panels and internal tools. It comes with a core headless package that provides different sets of hooks and components for dealing with concerns like data fetching, authentication, authorization, etc. It also has supplmentary packages which enable rapid development of React applications by integrating with various backend services like Airtable, Supabase and Strapi as well as UI frameworks like Ant Design, Material UI, Chakra UI and Mantine.
Architecture
Refine separates app concerns such as data fetching, authentication, access control, etc., into layers of React contexts each backed by a provider object, a set of corresponding hooks as well as relevant components. For example, the data layer represents a context dependent on a dataProvider object with a set of methods for handling CRUD actions. The data layer is accessed with a set of data hooks that help invoke the CRUD methods from UI components.
This means, we would have all CRUD related methods such as getList(), create(), show(), update() and delete() inside a dataProvider object and we are able to access them from a UI component using useList(), useCreate(), etc., data hooks. The data hooks, in turn, make use of React Query for data fetching, caching state management and error handling.
The Refine data hooks mentioned above are basically core hooks. Higher level hooks which are built top of these hooks exist, such as the useTable() hook provided by @refinedev/react-table support package that integrates React Table with Refine core. Higher level hooks adds additional features that increase development efficiency. For example, the useList() hook is employed by the useTable() hook that helps present data in a table using all the features of React Table. Similarly, the useCreate() core data hook is utilized inside the useForm() high level hook provided by the @refinedev/react-hook-form package which augments form related CRUD actions with React Hook Form.
Resource Definitions
Refine's resource definitions are specified inside the resources object. The resources object is passed to the resources prop of the <Refine /> component. Resource definitions, in combination with route definitions, set up a Refine app's nav menu items, their navigation URLs, as well as breadcrumbs, and help infer the default resource name of a CRUD page along a route.
Routing
Routing in Refine is supported by the react-router-dom package. Refinev4 supports explicit routing by delegating everything related to routing to the React Router APIs.
Inferencer
Refine's Inferencer is a powerful tool for quickly scaffolding CRUD pages and automatically generating code for a resource page. The Inferencer works by first polling a particular API endpoint to get the shape of the data and then placing all the hooks and UI elements necessary to fetch and present the data on a page.
UI Framework Integration
Refine's core package is designed to be "headless" which gives the freedom to integrate it with any UI component library or framework.
What is daisyUI?
daisyUI is an open source UI library built on top of TailwindCSS. It provides short, component-oriented, semantic classes composed from regular, longer Tailwind class strings that typically contribute to clumsy markup in an application. daisyUI hosts a growing collection of pre-styled templates for components like buttons, menus, and tabs with responsive, size, shape, and color variants.
Composing responsive, color, size, and shape variant classes manually with the @apply directive is practically inefficient with plain TailwindCSS classes. daisyUI does this out-of-the-box. On top of that, these component styles can be overridden or extended with the usual TailwindCSS utilities. As a result, daisyUI offers the convenience of using smaller class names, a smaller CSS file size, configurable number of variants, and greater customization without compromising much of the code quality.
Feel free to check out the daisyUI documentation to learn more.
Initialize a Refine App
For this app, we are going to start with Refine's headless core, using create refine-app to scaffold our pages and generate the initial page code. We will then make necessary logic and UI adjustments and then apply daisyUI classes to our components.
So, let's get started with initializing the Refine app first.
We'll create a local repository by using the create refine-app CLI-based app scaffolder. Run the following npm command from the directory of your choice to interactively initialize the project.
npm create refine-app@latest refine-daisyui
Select the following options when prompted:
✔ Choose a project template · refine-react
✔ What would you like to name your project?: · refine-daisyui
✔ Choose your backend service to connect: · REST API
✔ Do you want to use a UI Framework?: · Headless
✔ Do you want to add example pages?: · no
✔ Do you need i18n (Internationalization) support?: · No
✔ Choose a package manager: · npm
✔ Would you mind sending us your choices so that we can improve create refine-app? · yes
Take a note of the Headless choice. We are asking for Refine core package with plain JSX markup.
After completing the app initialization, let's navigate to the project folder and start our app with:
npm run dev
We should be greeted with the app's Welcome page.
Chores
We'll replace the Fake REST API with Fine Foods URL in the dataProvider prop. Update the App.tsx file to the following:
import { ErrorComponent, GitHubBanner, Refine } from "@refinedev/core";
import { RefineKbar, RefineKbarProvider } from "@refinedev/kbar";
import routerBindings, {
DocumentTitleHandler,
NavigateToResource,
UnsavedChangesNotifier,
} from "@refinedev/react-router-v6";
import dataProvider from "@refinedev/simple-rest";
import { BrowserRouter, Outlet, Route, Routes } from "react-router-dom";
import "./App.css";
import { Layout } from "./components/layout";
function App() {
return (
<BrowserRouter>
<GitHubBanner />
<RefineKbarProvider>
<Refine
dataProvider={dataProvider("https://api.finefoods.refine.dev")}
routerProvider={routerBindings}
options={{
syncWithLocation: true,
warnWhenUnsavedChanges: true,
}}
>
<Routes>
<Route
element={
<Layout>
<Outlet />
</Layout>
}
>
<Route path="*" element={<ErrorComponent />} />
</Route>
</Routes>
<RefineKbar />
<UnsavedChangesNotifier />
<DocumentTitleHandler />
</Refine>
</RefineKbarProvider>
</BrowserRouter>
);
}
export default App;
With these changes, we'll start fresh towards building the dashboard page first and then later move on to the CRUD pages for products and categories resources. At this point, we don't have any resources or their pages.
Notice, we are now using the Fine Foods REST API in the dataProvider prop of <Refine />.
The Fine Foods API is an example of the REST API hosted by Refine with a collection of end points. In this app, we will be querying the /dailyRevenue, /dailyOrders, /newCustomers and /orders endpoints for fetching data for our dashboard page. Later on, we'll also be accessing its /products and /categories endpoints for our resource pages.
daisyUI Installation
We are using daisyUI as our UI library. In order to integrate daisyUI into our Refine app, we have to first perform a Vite installation of TailwindCSS, its dependencies, and set up their configurations.
Go ahead an follow the below steps to first add TailwindCSS, PostCSS and Autoprefixer packages and then initialize tailwind.config.js:
Install TailwindCSS and related packages
- Run the following commands:
npm install -D tailwindcss postcss autoprefixer
npx tailwindcss init -p
- Inside
tailwind.config.jsfile, add file paths for scanning and applying TailwindCSS classes:
/** @type {import('tailwindcss').Config} */
export default {
content: ["./index.html", "./src/**/*.{js,ts,jsx,tsx}"],
theme: {
extend: {},
},
plugins: [],
};
- Modify the
App.cssto add TailwindCSS directives. It is important that we add them towards the top before any Tailwind style declarations. Copy over the CSS below:
Show App.css styles
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
margin: 0px;
}
/* TailwindCSS layers towards the top */
@tailwind base;
@tailwind components;
@tailwind utilities;
.layout {
display: flex;
gap: 16px;
}
@media screen and (max-width: 751px) {
.layout {
display: block;
}
}
.layout .content {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
flex-grow: 1;
}
.breadcrumb {
display: flex;
gap: 24px;
list-style-type: "/ ";
padding: 8px 16px;
border-bottom: 1px solid lightgray;
}
.breadcrumb a {
color: blue;
text-decoration: none;
}
.menu {
flex-shrink: 0;
padding: 8px 16px;
border-right: 1px solid lightgray;
}
.menu a {
color: black;
}
.menu .active {
font-weight: bold;
}
@media screen and (max-width: 751px) {
.menu {
border-right: none;
border-bottom: 1px solid lightgray;
}
}
.menu ul {
padding-left: 16px;
}
.page-container {
@apply mx-auto my-2 py-2 px-4 bg-slate-50 border rounded drop-shadow-md;
}
.page-title {
@apply text-xl font-bold;
}
.page-header {
@apply py-4 flex justify-between items-center mb-6;
}
We'll be using the custom classes in this App.css, so feel free to copy it over.
If you need a hand with TailwindCSS installation, please follow this guide for installing TailwindCSS with Vite
Install and setup daisyUI
With TailwindCSS set up properly, it's now turn to install and configure daisyUI.
- Install daisyUI with the following command:
npm install -D daisyui@latest
- And then add daisyUI as a plugin to
tailwind.config.js. Extend the daisyUIlighttheme and update theprimarycolor:
/** @type {import('tailwindcss').Config} */
export default {
content: ["./index.html", "./src/**/*.{js,ts,jsx,tsx}"],
daisyui: {
themes: [
{
light: {
...require("daisyui/src/theming/themes")["[data-theme=light]"],
primary: "#0d89ec",
},
},
],
},
theme: {
extend: {},
},
plugins: [require("daisyui")],
};
More details on customizing a daisyUI theme is available on the docs here
After these changes, with the server running, TailwindCSS watches for the use of daisyUI and TailwindCSS classes, and automatically compiles updated styles.
Other Packages
We have to install Refine's support packages for React Table and React Hook Form. We are using Tailwind Heroicons for our icons, the Day.js library for time calculations and Recharts library to plot our charts for KPI data. So, run the following and we are good to go:
npm install @refinedev/react-table @refinedev/react-hook-form @heroicons/react dayjs recharts
Interfaces
We'll be using the following interfaces throughout the app. So, feel free to copy and paste them over to src/interfaces/index.ts or a similar location.
src/interfaces/index.ts
export interface IOrder {
id: number;
user: IUser;
createdAt: string;
status: IOrderStatus;
address: IAddress;
amount: number;
}
export interface IUser {
id: number;
fullName: string;
gender: string;
gsm: string;
createdAt: string;
addresses: IAddress[];
}
export interface IOrderStatus {
id: number;
text: "Pending" | "Ready" | "On The Way" | "Delivered" | "Cancelled";
}
export interface IAddress {
text: string;
coordinate: [string, string];
}
export interface IChartDatum {
date: string;
value: string;
}
export interface IChart {
data: IChartDatum[];
total: number;
trend: number;
}
export interface IProduct {
id: number;
name: string;
isActive: boolean;
description: string;
createdAt: string;
price: number;
category: ICategory;
stock: number;
}
export interface ICategory {
id: number;
title: string;
isActive: boolean;
}
export type TTab = {
id: number;
label: string;
content: JSX.Element;
};
Building the Dashboard
Now that we have all the set up and packages ready, it's time for us to start building the dashboard page. The dashboard page will be displayed at the index route and contain KPI stats, charts and a table of data.
The <Dashboard /> Component
We'll add a /dashboard directory under src/pages and add the <Dashboard /> component to the index.tsx file under it.
Initially, it will return a dummy hero component. We'll update it in the coming sections.
import React from "react";
export const Dashboard: React.FC = () => {
return (
<div className="hero min-h-screen bg-base-200">
<div className="hero-content text-center">
<div className="max-w-md">
<h1 className="text-5xl font-bold">Hello there...</h1>
<p className="py-6">
You're here. A deva just as dashing and daisyuing - as yourself
refined
</p>
<button className="btn btn-primary">Buckle Up</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
};
We'll display the dashboard page at the /dashboard path and make it the index route. So, let's add the necessary resource and routes to the <Refine /> component in App.tsx.
Update the App.tsx as below:
Show updated App.tsx file
import { ErrorComponent, GitHubBanner, Refine } from "@refinedev/core";
import { RefineKbar, RefineKbarProvider } from "@refinedev/kbar";
import routerBindings, {
DocumentTitleHandler,
NavigateToResource,
UnsavedChangesNotifier,
} from "@refinedev/react-router-v6";
import dataProvider from "@refinedev/simple-rest";
import {
BrowserRouter,
Navigate,
Outlet,
Route,
Routes,
} from "react-router-dom";
import "./App.css";
import { Layout } from "./components/layout";
import { Dashboard } from "./pages/dashboard";
function App() {
return (
<BrowserRouter>
<GitHubBanner />
<RefineKbarProvider>
<Refine
dataProvider={dataProvider("https://api.finefoods.refine.dev")}
routerProvider={routerBindings}
resources={[
{
name: "dashboard",
list: "/dashboard",
},
]}
options={{
syncWithLocation: true,
warnWhenUnsavedChanges: true,
}}
>
<Routes>
<Route
element={
<Layout>
<Outlet />
</Layout>
}
>
<Route index element={<Navigate to="/dashboard" />} />
<Route path="/dashboard">
<Route index element={<Dashboard />} />
</Route>
<Route path="*" element={<ErrorComponent />} />
</Route>
</Routes>
<RefineKbar />
<UnsavedChangesNotifier />
<DocumentTitleHandler />
</Refine>
</RefineKbarProvider>
</BrowserRouter>
);
}
export default App;
We have updated our imports and passed the resources prop to <Refine />. We have defined a dashboard resource with only one page: the list. In the route definitions, as children to <Routes />, we have assigned the <Dashboard /> page to the /dashboard route and set it as the index route.
With these additions and changes, when we navigate to / or /dashboard, we should be able to see the dashboard page. It looks somewhat dashing like this:
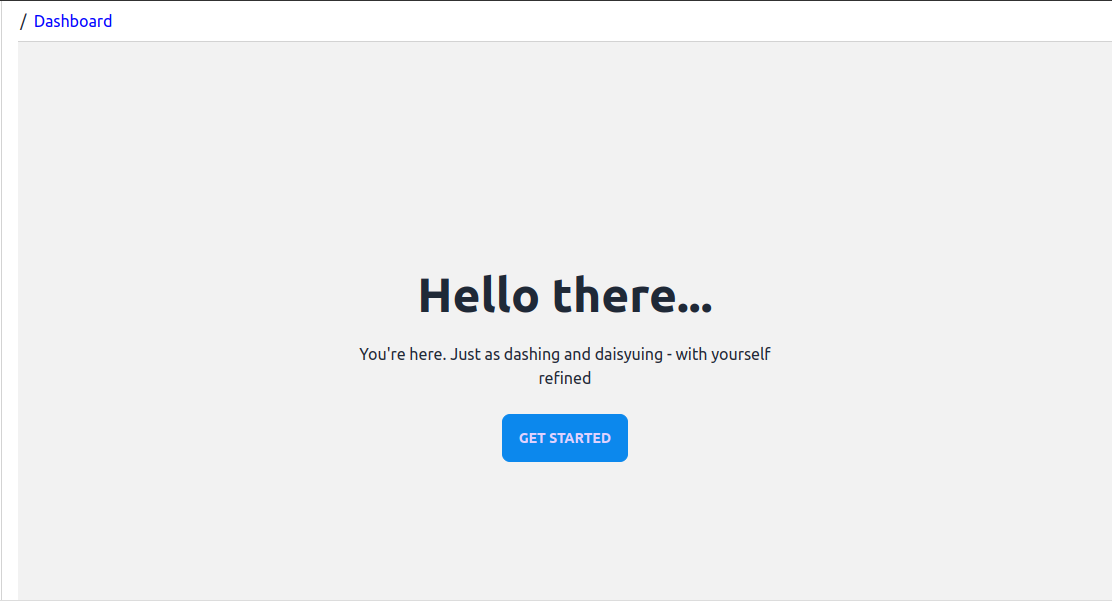
The <Stats /> Component
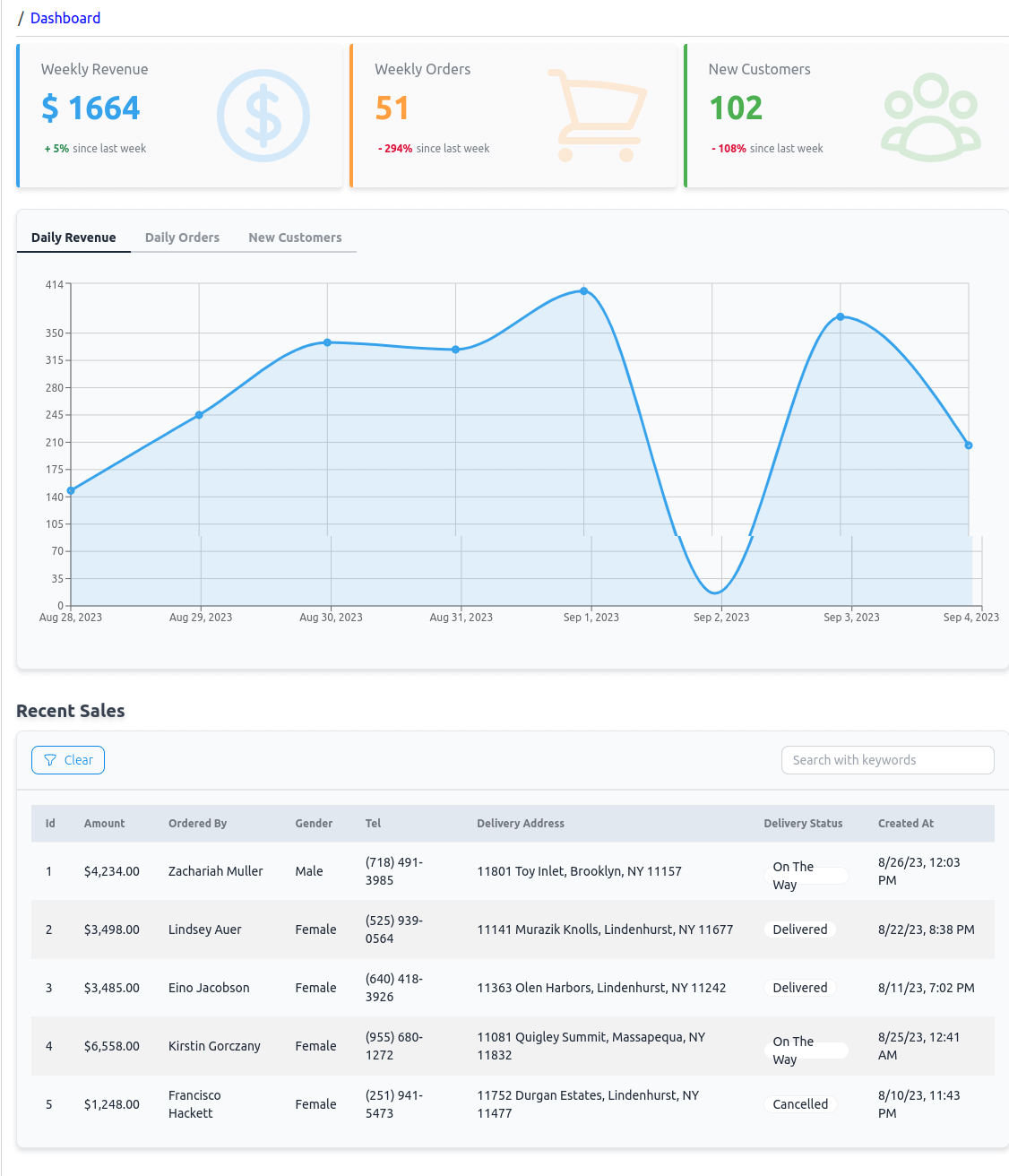
Let's now focus on implementing the features of the dashboard. Inside it, we'll have a <Stats /> component that takes in KPI data and returns a <KpiCard /> component for each. We'll create the <Stats /> component inside src/components/dashboard. And use the following code:
src/components/dashboard/Stats.tsx
import React from "react";
import { KpiCard } from "./KpiCard";
import { IChartDatum } from "../../interfaces";
import {
CurrencyDollarIcon,
ShoppingCartIcon,
UserGroupIcon,
} from "@heroicons/react/24/outline";
import { GetListResponse } from "@refinedev/core";
type TStats = {
dailyRevenue?: GetListResponse<IChartDatum>;
dailyOrders?: GetListResponse<IChartDatum>;
newCustomers?: GetListResponse<IChartDatum>;
};
const Stats = ({ dailyRevenue, dailyOrders, newCustomers }: TStats) => {
return (
<div className="w-full mx-auto mb-4 flex flex-col justify-center items-stretch md:flex-row md:justify-between drop-shadow-md">
<div className="w-full mx-auto md:flex-1 md:mr-2">
<KpiCard
title="Weekly Revenue"
data={dailyRevenue}
formatTotal={(value: number | string) => `$ ${value}`}
icon={<CurrencyDollarIcon className="h-32 w-32" />}
colors={{
stroke: "rgb(54, 162, 235)",
fill: "rgba(54, 162, 235, 0.2)",
}}
/>
</div>
<div className="w-full mx-auto md:flex-1">
<KpiCard
title="Weekly Orders"
data={dailyOrders}
icon={<ShoppingCartIcon className="h-32 w-32" />}
colors={{
stroke: "rgb(255, 159, 64)",
fill: "rgba(255, 159, 64, 0.2)",
}}
/>
</div>
<div className="w-full mx-auto md:flex-1 md:ml-2">
<KpiCard
title="New Customers"
data={newCustomers}
icon={<UserGroupIcon className="h-32 w-32" />}
colors={{
stroke: "rgb(76, 175, 80)",
fill: "rgba(76, 175, 80, 0.2)",
}}
/>
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default Stats;
The <Stats /> relays and displays KPI data inside the <KpiCard /> component, so let's work on that now.
<KpiCard /> Component
Let's create the <KpiCard /> component inside src/components/dashboard directory. The <KpiCard /> represents an individual stat item. It takes in a number of props and displays the KPI data with an icon. It looks like this:
src/components/dashboard/KpiCard.tsx
import React from "react";
type TKpiCardProps = {
title: string;
data: any;
icon: JSX.Element;
colors: {
stroke: string;
fill: string;
};
formatTotal?: (value: number | string) => typeof value;
};
export const KpiCard = ({
title,
data,
icon,
colors,
formatTotal = (value) => value,
}: TKpiCardProps) => {
const total = data?.data?.total;
const trend = data?.data?.trend;
const calc = Math.round((trend / total) * 100);
const percent = total > trend ? `+ ${calc}%` : `- ${calc}%`;
const textColor = total > trend ? "seagreen" : "crimson";
return (
<div
className="stat my-2 py-4 flex-1 bg-zinc-50 border-l-4 rounded"
style={{ borderColor: colors?.stroke }}
>
<div
className="stat-figure text-secondary"
style={{ color: colors?.fill }}
>
{icon}
</div>
<div className="stat-title text-l">{title}</div>
<div className="stat-value" style={{ color: colors?.stroke }}>
{formatTotal(total ?? "...")}
</div>
<div className="stat-desc my-2">
<span className="mx-1 text-l font-bold" style={{ color: textColor }}>
{percent}
</span>
since last week
</div>
</div>
);
};
Note that we have started using daisyUI classes in the <KpiCard /> component. stat, stat-figure, stat-title, stat-value, stat-desc are classes provided by the daisyUI Stats template.
With the <Stats /> and <KpiCard /> components completed, we are ready to update the <Dashboard /> component. Inside it, we will query a number of Fine Foods end points to gather revenue, orders and customers data and then transform them. We will pass the transformed data to child components, one by one as they get built.
For now, we'll import and display the <Stats /> component and pass it three sets of KPI data in order to display the KPI cards at the top of the dashboard page.
Replace the code inside the <Dashboard /> component with the following:
src/pages/dashboard/index.tsx
import React, { useMemo } from "react";
import { CrudFilter, useList } from "@refinedev/core";
import dayjs from "dayjs";
import Stats from "../../components/dashboard/Stats";
import { IChartDatum, TTab } from "../../interfaces";
const filters: CrudFilter[] = [
{
field: "start",
operator: "eq",
value: dayjs()?.subtract(7, "days")?.startOf("day"),
},
{
field: "end",
operator: "eq",
value: dayjs().startOf("day"),
},
];
export const Dashboard: React.FC = () => {
const { data: dailyRevenue } = useList<IChartDatum>({
resource: "dailyRevenue",
filters,
});
const { data: dailyOrders } = useList<IChartDatum>({
resource: "dailyOrders",
filters,
});
const { data: newCustomers } = useList<IChartDatum>({
resource: "newCustomers",
filters,
});
return (
<>
<Stats
dailyRevenue={dailyRevenue}
dailyOrders={dailyOrders}
newCustomers={newCustomers}
/>
</>
);
};
Notice we are fetching data from three Fine Foods API end points: /dailyRevenue, /dailyOrders and /newCustomers. We are fetching them with the useList() Refine core hook. We are querying them as resources although in our Refine admin panel app they are not. The filters object is used to get the past 7 days' data.
You can find more details in the Refine useList() docs here.
With these changes, our dashboard page has three KPI cards displayed at the top:
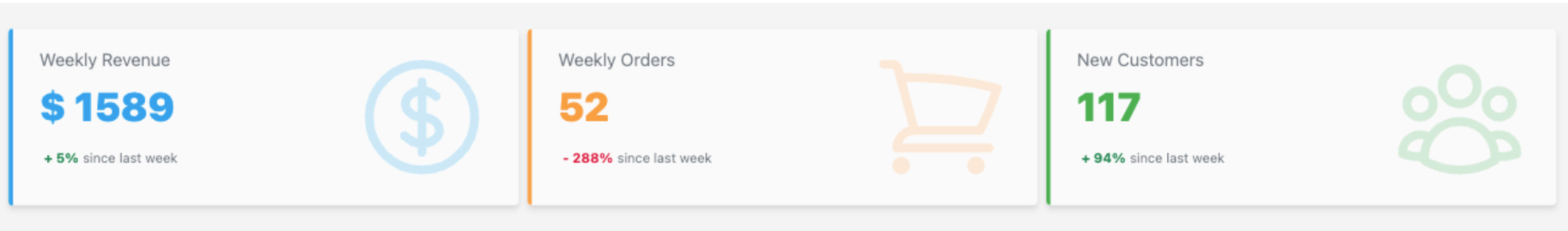
Tab Components
Now we want to display three charts inside a tabs panel below the KPI cards. So, we'll create the <TabItem />, <TabPanel /> and <TabView /> components inside the src/components/dashboard directory. We'll also create two chart components, a <ResponsiveAreaChart /> and a <ResponsiveBarChart /> to plot KPI data. Once all components are ready, we'll add the <TabView /> component to <Dashboard />.
The <TabView /> component will house the other two tab components, so in order to avoid linter and browser errors, we'll start with the children.
<TabItem /> Component
We need to have the <TabItem /> button for accessing a tab panel. So, create the <TabItem /> component as below:
src/components/dashboard/TabItem.tsx
import React from "react";
type TTabItem = {
label: string;
isActive: Boolean;
clickHandler: () => void;
};
export const TabItem = ({ label, isActive, clickHandler }: TTabItem) => {
return (
<a
className={`text-l font-bold tab tab-bordered${
isActive ? " tab-active" : ""
}`}
onClick={clickHandler}
>
{label}
</a>
);
};
<TabPanel /> Component
The <TabPanel /> will contain a chart which can be accessed by clicking on a <TabItem />. Let's go ahead and create the <TabPanel /> component with the following code:
src/components/dashboard/TabPanel.tsx
import React from "react";
type TTabPanelProps = {
isActive: Boolean;
children: JSX.Element;
};
export const TabPanel = ({ isActive, children }: TTabPanelProps) => {
return isActive ? <div className="mx-auto py-6">{children}</div> : null;
};
<TabView /> Component
The <TabView /> component will contain the tab view logic and state. It will accept the tabs object and display a <TabItem /> and <TabPanel > as children for each item in the tabs object. Let's create the <TabView /> component with the code below:
src/components/dashboard/TabView.tsx
import React, { useState } from "react";
import { TabItem } from "./TabItem";
import { TabPanel } from "./TabPanel";
import { TTab } from "../../interfaces";
type TTabViewProps = {
tabs: TTab[];
};
export const TabView = ({ tabs }: TTabViewProps) => {
const [activeTab, setActiveTab] = useState(0);
return (
<div className="mx-auto py-4 bg-slate-50 border rounded-lg drop-shadow-md">
<div className="tabs">
{tabs?.map((tab: TTab, index: number) => (
<TabItem
key={tab?.id}
label={tab?.label}
isActive={index === activeTab}
clickHandler={() => setActiveTab(index)}
/>
))}
</div>
<div className="mx-auto">
{tabs?.map((tab: TTab, index: number) => (
<TabPanel key={tab?.id} isActive={index === activeTab}>
{tab?.content}
</TabPanel>
))}
</div>
</div>
);
};
Recharts Plots
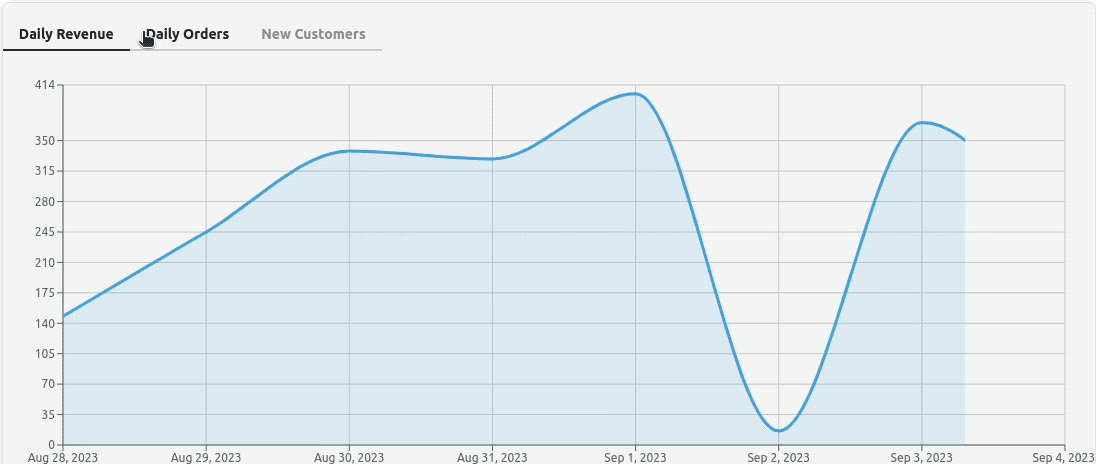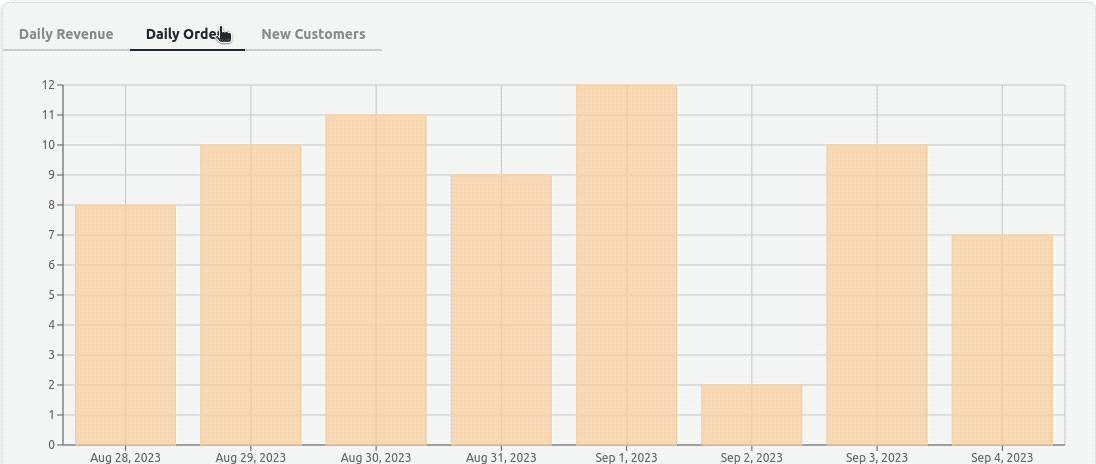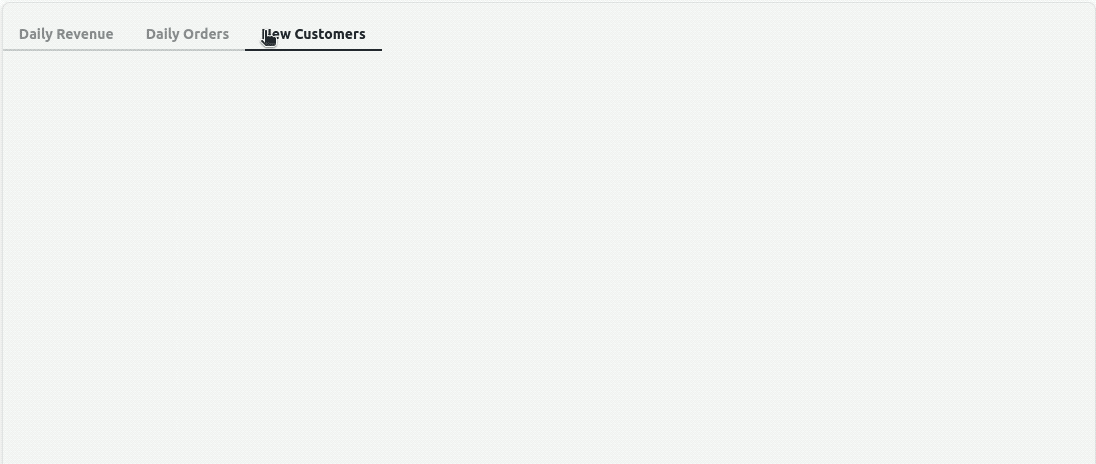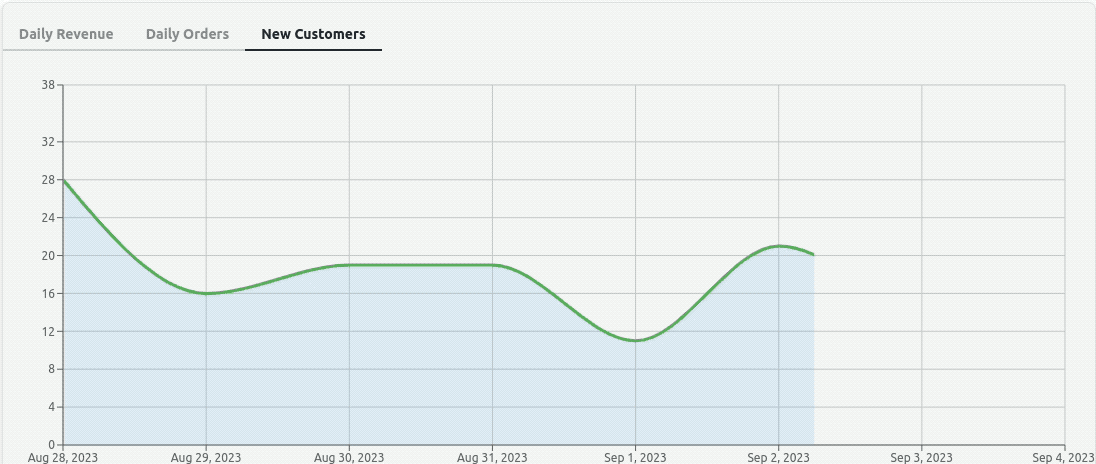
With the tab components ready, we need to create three charts to be displayed inside <TabView /> by mapping through the tabs object. We want to implement them using Recharts. One <ResponsiveAreaChart /> and one <ResponsiveBarChart />.
For plotting the data, <ResponsiveAreaChart /> will use the <AreaChart /> APIs of the Recharts library and <ResponsiveBarChart /> will use the <BarChart /> APIs. They both will use <ResponsiveContainer /> for responsiveness.
You can find all the details in the Rechats <AreaChart />, <BarChart /> and <ResponsiveContainer /> documentations if you need to.
We'll build the charts inside the src/components/dashboard directory.
Area Chart
Create the <ResponsiveAreaChart /> component with the code below:
src/components/dashboard/ResponsiveAreaChart.tsx
import React from "react";
import {
ResponsiveContainer,
AreaChart,
CartesianGrid,
XAxis,
YAxis,
Tooltip,
Area,
} from "recharts";
import { ChartTooltip } from "../../components/dashboard/ChartTooltip";
import { IChartDatum } from "../../interfaces";
type TResponsiveAreaChartProps = {
kpi: string;
data: IChartDatum[];
colors: {
stroke: string;
fill: string;
};
};
export const ResponsiveAreaChart = ({
kpi,
data,
colors,
}: TResponsiveAreaChartProps) => {
return (
<ResponsiveContainer height={400}>
<AreaChart
data={data}
height={400}
margin={{
top: 10,
right: 30,
left: 0,
bottom: 0,
}}
>
<CartesianGrid strokeDasharray="0 0 0" />
<XAxis
dataKey="date"
tickCount={data?.length ?? 0}
tick={{
stroke: "light-grey",
strokeWidth: 0.5,
fontSize: "12px",
}}
/>
<YAxis
tickCount={13}
tick={{
stroke: "light-grey",
strokeWidth: 0.5,
fontSize: "12px",
}}
interval="preserveStartEnd"
domain={[0, "dataMax + 10"]}
/>
<Tooltip
content={<ChartTooltip kpi={kpi} colors={colors} />}
wrapperStyle={{
backgroundColor: "rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.7)",
border: "0 solid #000",
borderRadius: "10px",
}}
/>
<Area
type="monotone"
dataKey="value"
stroke={colors?.stroke}
strokeWidth={3}
fill={colors?.fill}
dot={{
stroke: colors?.stroke,
strokeWidth: 3,
}}
/>
</AreaChart>
</ResponsiveContainer>
);
};
Inside <ResponsiveAreaChart /> we are receiving the data along with other props and relaying it to <AreaChart /> with its data={data} prop. We are using <XAxis />, <YAxis /> for ticks and axes labels. We are drawing the area and monotonic line with <Area /> component and its props. <CartesianGrid /> draws a grid in the background. We also have a custom tooltip shown inside <ToolTip />.
Bar Chart
In a similar way, create the <ResponsiveBarChart /> component with the below code:
src/components/dashboard/ResponsiveBarChart.tsx
import React from "react";
import {
ResponsiveContainer,
BarChart,
CartesianGrid,
XAxis,
YAxis,
Tooltip,
Bar,
} from "recharts";
import { ChartTooltip } from "../../components/dashboard/ChartTooltip";
import { IChartDatum } from "../../interfaces";
type TResponsiveBarChartProps = {
kpi: string;
data: IChartDatum[];
colors: {
stroke: string;
fill: string;
};
};
export const ResponsiveBarChart = ({
kpi,
data,
colors,
}: TResponsiveBarChartProps) => {
return (
<ResponsiveContainer height={400}>
<BarChart
data={data}
width={1200}
height={400}
margin={{
top: 10,
right: 30,
left: 0,
bottom: 0,
}}
>
<CartesianGrid strokeDasharray="0 0" />
<XAxis
dataKey="date"
tickCount={data?.length ?? 0}
tick={{
stroke: "light-grey",
strokeWidth: 0.5,
fontSize: "12px",
}}
/>
<YAxis
domain={[0, "dataMax"]}
tickCount={13}
tick={{
stroke: "light-grey",
strokeWidth: 0.5,
fontSize: "12px",
}}
/>
<Tooltip
content={<ChartTooltip colors={colors} kpi={kpi} />}
wrapperStyle={{
backgroundColor: "rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.7)",
border: "0 solid #000",
borderRadius: "10px",
}}
/>
<Bar
type="monotone"
dataKey="value"
stroke="rgb(255, 207, 159)"
strokeWidth={1}
fill="rgba(255, 207, 159, 0.7)"
/>
</BarChart>
</ResponsiveContainer>
);
};
<ResponsiveBarChart /> does the same thing as <ResponsiveAreaChart />, except that it draws a bar chart with Recharts <BarChart /> component.
Custom Tooltip
The charts above use a custom tooltip, the <ChartTooltip /> component, to show data point details according to the mouse position.
Let's create the <ChartTooltip /> component with the following code:
src/components/dashboard/ChartTooltip.tsx
import React from "react";
export const ChartTooltip = ({
active,
payload,
label,
coordinate,
colors,
kpi,
}: any) => {
if (active && payload && payload.length) {
const dataPoint = payload[0].payload;
const tooltipStyle = {
left: coordinate.x, // Adjust positioning
top: coordinate.y, // Adjust positioning
};
return (
<div
className="p-1 flex flex-col justify-center items-start border border-black rounded-lg text-zinc-50"
style={tooltipStyle}
>
<div
style={{
position: "absolute",
width: "0",
height: "0",
borderTop: "10px solid transparent",
borderBottom: "10px solid transparent",
borderRight: "10px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.7)",
left: "-10px",
}}
/>
<p className="flex text-xs font-semibold">{label}</p>
<p className="text-xs">
<span
className="mr-1"
style={{
width: "0.5px",
height: "0.5px",
border: `1px solid ${colors?.stroke}`,
backgroundColor: colors?.fill,
}}
>
</span>
{`${kpi}: ${dataPoint.value}`}
</p>
</div>
);
}
return null;
};
Now we have all the components for displaying <TabView /> ready. So, we'll import and display it inside the dashboard below <Stats />. Let's update the <Dashboard /> component with the below code:
src/pages/dashboard/index.tsx
import React, { useMemo } from "react";
import { CrudFilter, useList } from "@refinedev/core";
import dayjs from "dayjs";
import Stats from "../../components/dashboard/Stats";
import { ResponsiveAreaChart } from "../../components/dashboard/ResponsiveAreaChart";
import { ResponsiveBarChart } from "../../components/dashboard/ResponsiveBarChart";
import { TabView } from "../../components/dashboard/TabView";
import { IChartDatum, TTab } from "../../interfaces";
const filters: CrudFilter[] = [
{
field: "start",
operator: "eq",
value: dayjs()?.subtract(7, "days")?.startOf("day"),
},
{
field: "end",
operator: "eq",
value: dayjs().startOf("day"),
},
];
export const Dashboard: React.FC = () => {
const { data: dailyRevenue } = useList<IChartDatum>({
resource: "dailyRevenue",
filters,
});
const { data: dailyOrders } = useList<IChartDatum>({
resource: "dailyOrders",
filters,
});
const { data: newCustomers } = useList<IChartDatum>({
resource: "newCustomers",
filters,
});
const useMemoizedChartData = (d: any) => {
return useMemo(() => {
return d?.data?.data?.map((item: IChartDatum) => ({
date: new Intl.DateTimeFormat("en-US", {
month: "short",
year: "numeric",
day: "numeric",
}).format(new Date(item.date)),
value: item?.value,
}));
}, [d]);
};
const memoizedRevenueData = useMemoizedChartData(dailyRevenue);
const memoizedOrdersData = useMemoizedChartData(dailyOrders);
const memoizedNewCustomersData = useMemoizedChartData(newCustomers);
const tabs: TTab[] = [
{
id: 1,
label: "Daily Revenue",
content: (
<ResponsiveAreaChart
kpi="Daily revenue"
data={memoizedRevenueData}
colors={{
stroke: "rgb(54, 162, 235)",
fill: "rgba(54, 162, 235, 0.2)",
}}
/>
),
},
{
id: 2,
label: "Daily Orders",
content: (
<ResponsiveBarChart
kpi="Daily orders"
data={memoizedOrdersData}
colors={{
stroke: "rgb(255, 159, 64)",
fill: "rgba(255, 159, 64, 0.7)",
}}
/>
),
},
{
id: 3,
label: "New Customers",
content: (
<ResponsiveAreaChart
kpi="New customers"
data={memoizedNewCustomersData}
colors={{
stroke: "rgb(76, 175, 80)",
fill: "rgba(54, 162, 235, 0.2)",
}}
/>
),
},
];
return (
<>
<Stats
dailyRevenue={dailyRevenue}
dailyOrders={dailyOrders}
newCustomers={newCustomers}
/>
<TabView tabs={tabs} />
</>
);
};
Notice we are defining a useMemoizedChartData() hook to transform the fetched data and memoize them to make them chart ready. We are then setting the tabs object from the data, the charts, and other properties. We eventually pass the tabs object to the <TabView /> component.
With these changes, our dashboard page displays a panel of charts accessible from a top tabbed menu:
<RecentSales /> Component
Lastly, we want to display recent sales data in a table below the charts. We have the <RecentSales /> component that lists recent orders in a table with filtering and sorting features. Let's create the <RecentSales /> component with the following code:
src/components/dashboard/RecentSales.tsx
import React, { useMemo, useRef } from "react";
import { getDefaultFilter } from "@refinedev/core";
import { useTable } from "@refinedev/react-table";
import { ColumnDef, flexRender } from "@tanstack/react-table";
import {
FunnelIcon,
BarsArrowDownIcon,
BarsArrowUpIcon,
} from "@heroicons/react/24/outline";
export const RecentSales = () => {
const filterForm: any = useRef(null);
const columns = useMemo<ColumnDef<any>[]>(
() => [
{
id: "id",
accessorKey: "id",
header: "Id",
},
{
id: "amount",
accessorKey: "amount",
header: "Amount",
cell: function render({ getValue }) {
const amountCur = new Intl.NumberFormat("en-US", {
style: "currency",
currency: "USD",
}).format(getValue() as number);
return <div>{amountCur}</div>;
},
},
{
id: "orderedBy",
accessorKey: "user.fullName",
header: "Ordered By",
},
{
id: "gender",
accessorKey: "user.gender",
header: "Gender",
},
{
id: "tel",
accessorKey: "user.gsm",
enableSorting: false,
header: "Tel",
},
{
id: "deliveryAddress",
accessorKey: "address.text",
header: "Delivery Address",
},
{
id: "deliveryStatus",
accessorKey: "status.text",
header: "Delivery Status",
cell: function render({ getValue }) {
type TSaleStatusStyleMap = {
[key: string]: string;
};
const saleStatusStyleMap: TSaleStatusStyleMap = {
Cancelled: "error",
Ready: "primary",
"On The Way": "info",
Pending: "warning",
Delivered: "success",
};
const status = getValue() as string;
const daisyBadgeClasses = () =>
"badge badge-" + saleStatusStyleMap[status];
return <div className={daisyBadgeClasses()}>{status}</div>;
},
},
{
id: "createdAt",
accessorKey: "createdAt",
header: "Created At",
cell: function render({ getValue }) {
const date = new Intl.DateTimeFormat("en-US", {
dateStyle: "short",
timeStyle: "short",
}).format(new Date(getValue() as string));
return <div>{date}</div>;
},
},
],
[],
);
const {
refineCore: { filters, setCurrent, setFilters },
getHeaderGroups,
getRowModel,
} = useTable({
refineCoreProps: {
resource: "orders",
pagination: {
pageSize: 5,
},
},
columns,
});
const header = (
<div className="w-full mx-auto">
<div className="my-2">
<h1 className="page-title text-gray-700">Recent Sales</h1>
</div>
<div className="overflow-x-auto bg-slate-50 border rounded-t-lg">
<div className="flex justify-between items-center m-4">
<button
className="btn btn-outline btn-primary btn-sm normal-case font-light"
onClick={() => {
setCurrent(1);
setFilters([], "replace");
filterForm?.current?.reset();
}}
>
<FunnelIcon className="h-4 w-4" />
Clear
</button>
<div className="flex justify-end items-center">
<form ref={filterForm}>
<input
className="input input-bordered input-sm"
type="search"
value={getDefaultFilter("q", filters)}
onChange={(e) => {
setCurrent(1);
setFilters([
{
field: "q",
value: e.target.value,
operator: "contains",
},
]);
}}
placeholder="Search with keywords"
/>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
return (
<div className="w-full mx-auto my-8 drop-shadow-md">
{header}
<div className="p-4 overflow-x-auto bg-slate-50 border rounded-b-lg">
<table className="table table-zebra border-t">
<thead className="bg-slate-200">
{getHeaderGroups()?.map((headerGroup) => (
<tr key={headerGroup?.id}>
{headerGroup?.headers?.map((header) => (
<th
className="hover:bg-slate-300"
key={header?.id}
onClick={header?.column?.getToggleSortingHandler()}
>
<div className="flex justify-start items-center">
{!header?.isPlaceholder &&
flexRender(
header?.column?.columnDef?.header,
header?.getContext(),
)}
{{
asc: <BarsArrowUpIcon className="h-4 w-4" />,
desc: <BarsArrowDownIcon className="h-4 w-4" />,
}[header?.column?.getIsSorted() as string] ?? null}
</div>
</th>
))}
</tr>
))}
</thead>
<tbody>
{getRowModel()?.rows?.map((row) => (
<tr key={row?.id}>
{row?.getVisibleCells()?.map((cell) => (
<td key={cell?.id}>
{flexRender(
cell?.column?.columnDef?.cell,
cell?.getContext(),
)}
</td>
))}
</tr>
))}
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
);
};
In the <RecentSales /> component, we are using a useTable() hook, which is a high level hook provided by Refine's React Table supported @refinedev/react-table package. It queries the /orders endpoint and implements a table with filtering and sorting features.
We'll come to the details of useTable() when we create list pages for products and categories resources.
With the <RecentSales /> component ready, let's import it and display it inside <Dashboard />. Update it with the following code:
Show Dashboard code
import React, { useMemo } from "react";
import { CrudFilter, useList } from "@refinedev/core";
import dayjs from "dayjs";
import Stats from "../../components/dashboard/Stats";
import { ResponsiveAreaChart } from "../../components/dashboard/ResponsiveAreaChart";
import { ResponsiveBarChart } from "../../components/dashboard/ResponsiveBarChart";
import { TabView } from "../../components/dashboard/TabView";
import { RecentSales } from "../../components/dashboard/RecentSales";
import { IChartDatum, TTab } from "../../interfaces";
const filters: CrudFilter[] = [
{
field: "start",
operator: "eq",
value: dayjs()?.subtract(7, "days")?.startOf("day"),
},
{
field: "end",
operator: "eq",
value: dayjs().startOf("day"),
},
];
export const Dashboard: React.FC = () => {
const { data: dailyRevenue } = useList<IChartDatum>({
resource: "dailyRevenue",
filters,
});
const { data: dailyOrders } = useList<IChartDatum>({
resource: "dailyOrders",
filters,
});
const { data: newCustomers } = useList<IChartDatum>({
resource: "newCustomers",
filters,
});
const useMemoizedChartData = (d: any) => {
return useMemo(() => {
return d?.data?.data?.map((item: IChartDatum) => ({
date: new Intl.DateTimeFormat("en-US", {
month: "short",
year: "numeric",
day: "numeric",
}).format(new Date(item.date)),
value: item?.value,
}));
}, [d]);
};
const memoizedRevenueData = useMemoizedChartData(dailyRevenue);
const memoizedOrdersData = useMemoizedChartData(dailyOrders);
const memoizedNewCustomersData = useMemoizedChartData(newCustomers);
const tabs: TTab[] = [
{
id: 1,
label: "Daily Revenue",
content: (
<ResponsiveAreaChart
kpi="Daily revenue"
data={memoizedRevenueData}
colors={{
stroke: "rgb(54, 162, 235)",
fill: "rgba(54, 162, 235, 0.2)",
}}
/>
),
},
{
id: 2,
label: "Daily Orders",
content: (
<ResponsiveBarChart
kpi="Daily orders"
data={memoizedOrdersData}
colors={{
stroke: "rgb(255, 159, 64)",
fill: "rgba(255, 159, 64, 0.7)",
}}
/>
),
},
{
id: 3,
label: "New Customers",
content: (
<ResponsiveAreaChart
kpi="New customers"
data={memoizedNewCustomersData}
colors={{
stroke: "rgb(76, 175, 80)",
fill: "rgba(54, 162, 235, 0.2)",
}}
/>
),
},
];
return (
<>
<Stats
dailyRevenue={dailyRevenue}
dailyOrders={dailyOrders}
newCustomers={newCustomers}
/>
<TabView tabs={tabs} />
<RecentSales />
</>
);
};
With all these updates, we have completed implementing the dashboard page. It now looks like this:
Adding CRUD Pages
Having completed the dashboard page above, in this section, we'll add CRUD pages for products and categories resources. We'll start implementing the pages for the products resource first.
Product Pages
We want list, create, edit and show pages for the products. Since we are using Refine's headless core without any supported UI library, it helps if we use the Inferencer to generate the pages for us. We'll leverage the power of Refine's <HeadlessInferencer /> component in the CRUD pages.
There are two steps to getting the Inferencer generated page code:
Scaffold the CRUD pages by running the Inferencer to implement all the
productspages with<HeadlessInferencer />.<HeadlessInferencer />then generates the actual codes for us that we can get from the page in the browser.Navigate along the
/productspath to an action route in your browser and get the code from the page by clicking on theShow the auto-generated codebutton. It is graciously provided to us by Refine 😄
We'll scaffold the pages first with the following Inferencer command:
npm run refine create-resource product
This produces <ProductList />, <ProductCreate />, <ProductEdit /> and <ProductShow /> pages. You can find them under a pluralized /products directory inside src/pages.
This also automatically generates the resource definition for products and adds it to the resources array in App.tsx. Resource paths for list, create, show and edit are specified:
resources={[
{
name: "products",
list: "/product",
create: "/product/create",
edit: "/product/edit/:id",
show: "/product/show/:id",
}
]}
We have to manually add the route definitions for each action individually to the App.tsx file. So, the updated App.tsx should have the following changes with resources and routes definitions added for products:
Show latest App.tsx code
import { ErrorComponent, GitHubBanner, Refine } from "@refinedev/core";
import { RefineKbar, RefineKbarProvider } from "@refinedev/kbar";
import routerBindings, {
DocumentTitleHandler,
NavigateToResource,
UnsavedChangesNotifier,
} from "@refinedev/react-router-v6";
import dataProvider from "@refinedev/simple-rest";
import {
BrowserRouter,
Navigate,
Outlet,
Route,
Routes,
} from "react-router-dom";
import "./App.css";
import { Layout } from "./components/layout";
import { Dashboard } from "./pages/dashboard";
import {
ProductList,
ProductCreate,
ProductEdit,
ProductShow,
} from "./pages/products";
function App() {
return (
<BrowserRouter>
<GitHubBanner />
<RefineKbarProvider>
<Refine
dataProvider={dataProvider("https://api.finefoods.refine.dev")}
routerProvider={routerBindings}
resources={[
{
name: "dashboard",
list: "/dashboard",
},
{
name: "products",
list: "/products",
create: "/products/create",
edit: "/products/edit/:id",
show: "/products/show/:id",
meta: {
canDelete: true,
},
},
]}
options={{
syncWithLocation: true,
warnWhenUnsavedChanges: true,
}}
>
<Routes>
<Route
element={
<Layout>
<Outlet />
</Layout>
}
>
<Route index element={<Navigate to="/dashboard" />} />
<Route path="/dashboard">
<Route index element={<Dashboard />} />
</Route>
<Route path="/products">
<Route index element={<ProductList />} />
<Route path="create" element={<ProductCreate />} />
<Route path="edit/:id" element={<ProductEdit />} />
<Route path="show/:id" element={<ProductShow />} />
</Route>
<Route path="*" element={<ErrorComponent />} />
</Route>
</Routes>
<RefineKbar />
<UnsavedChangesNotifier />
<DocumentTitleHandler />
</Refine>
</RefineKbarProvider>
</BrowserRouter>
);
}
export default App;
Notice towards the top that we have imported the scaffolded components (the ones with <HeadlessInferencer /> component, not yet the actual page code). Towards the end, we assigned them to /products paths for defining the routes. Routine React Router DOM stuff.
With the above changes, we have added possible actions and their routes for the products resource. We defined the routes and pages for list, create, edit and show actions and have enabled delete action as well. The page mapping for each route are handled with the <Route /> component.
Refine maps resource paths to page components via route definitions, and using the map infers the resource name of a page at the current URL of the browser. That way, hooks like useTable() and useNavigation(), and Inferencer components like <HeadlessInferencer /> are always able to infer the default resource name from inside a resource page.
You can find more information about resources and routing on the Refine documentation.
Now when we navigate along the /products paths, we can see some clumsy looking pages in need of proper styling. So, we're interested in getting their code and modifying them according to our needs. We are going to do that one by one in the following sections.
<ProductList /> Page
To begin with, the scaffolded <ProductList /> component looks like this:
import { IResourceComponentsProps } from "@refinedev/core";
import { HeadlessInferencer } from "@refinedev/inferencer/headless";
export const ProductList: React.FC<IResourceComponentsProps> = () => {
return <HeadlessInferencer />;
};
The <HeadlessInferencer /> infers the resource name and action path from the resource and routes definitions based on the current URL of the browser. It then polls the Fine Foods /products end point to figure out the data shape, and based on the shape, it uses the necessary refine-React Table APIs and JSX markup to present the fetched data in a table.
We'll grab the generated code from the page modal by clicking on the Show the auto-generated code button. It is pretty diligent and should look something like this:
Show auto-generated ProductList code
import React from "react";
import { IResourceComponentsProps, useNavigation } from "@refinedev/core";
import { useTable } from "@refinedev/react-table";
import { ColumnDef, flexRender } from "@tanstack/react-table";
export const ProductList: React.FC<IResourceComponentsProps> = () => {
const columns = React.useMemo<ColumnDef<any>[]>(
() => [
{
id: "id",
accessorKey: "id",
header: "Id",
},
{
id: "name",
accessorKey: "name",
header: "Name",
},
{
id: "isActive",
accessorKey: "isActive",
header: "Is Active",
cell: function render({ getValue }) {
return getValue<any>() ? "yes" : "no";
},
},
{
id: "description",
accessorKey: "description",
header: "Description",
},
{
id: "images",
accessorKey: "images",
header: "Images",
cell: function render({ getValue }) {
return (
<ul>
{getValue<any[]>()?.map((item, index) => (
<li key={index}>{item?.url}</li>
))}
</ul>
);
},
},
{
id: "createdAt",
accessorKey: "createdAt",
header: "Created At",
cell: function render({ getValue }) {
return new Date(getValue<any>()).toLocaleString(undefined, {
timeZone: "UTC",
});
},
},
{
id: "price",
accessorKey: "price",
header: "Price",
},
{
id: "category",
accessorKey: "category.title",
header: "Category",
},
{
id: "actions",
accessorKey: "id",
header: "Actions",
cell: function render({ getValue }) {
return (
<div
style={{
display: "flex",
flexDirection: "row",
flexWrap: "wrap",
gap: "4px",
}}
>
<button
onClick={() => {
show("products", getValue() as string);
}}
>
Show
</button>
<button
onClick={() => {
edit("products", getValue() as string);
}}
>
Edit
</button>
</div>
);
},
},
],
[],
);
const { edit, show, create } = useNavigation();
const {
getHeaderGroups,
getRowModel,
setOptions,
refineCore: {
tableQueryResult: { data: tableData },
},
getState,
setPageIndex,
getCanPreviousPage,
getPageCount,
getCanNextPage,
nextPage,
previousPage,
setPageSize,
getColumn,
} = useTable({
columns,
});
setOptions((prev) => ({
...prev,
meta: {
...prev.meta,
},
}));
return (
<div style={{ padding: "16px" }}>
<div
style={{
display: "flex",
alignItems: "center",
justifyContent: "space-between",
}}
>
<h1>Products</h1>
<button onClick={() => create("products")}>Create</button>
</div>
<div style={{ maxWidth: "100%", overflowY: "scroll" }}>
<table>
<thead>
{getHeaderGroups().map((headerGroup) => (
<tr key={headerGroup.id}>
{headerGroup.headers.map((header) => (
<th key={header.id}>
{!header.isPlaceholder &&
flexRender(
header.column.columnDef.header,
header.getContext(),
)}
</th>
))}
</tr>
))}
</thead>
<tbody>
{getRowModel().rows.map((row) => (
<tr key={row.id}>
{row.getVisibleCells().map((cell) => (
<td key={cell.id}>
{flexRender(cell.column.columnDef.cell, cell.getContext())}
</td>
))}
</tr>
))}
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
<div style={{ marginTop: "12px" }}>
<button
onClick={() => setPageIndex(0)}
disabled={!getCanPreviousPage()}
>
{"<<"}
</button>
<button onClick={() => previousPage()} disabled={!getCanPreviousPage()}>
{"<"}
</button>
<button onClick={() => nextPage()} disabled={!getCanNextPage()}>
{">"}
</button>
<button
onClick={() => setPageIndex(getPageCount() - 1)}
disabled={!getCanNextPage()}
>
{">>"}
</button>
<span>
<strong>
{" "}
{getState().pagination.pageIndex + 1} / {getPageCount()}{" "}
</strong>
</span>
<span>
| Go to Page:{" "}
<input
type="number"
defaultValue={getState().pagination.pageIndex + 1}
onChange={(e) => {
const page = e.target.value ? Number(e.target.value) - 1 : 0;
setPageIndex(page);
}}
/>
</span> <select
value={getState().pagination.pageSize}
onChange={(e) => {
setPageSize(Number(e.target.value));
}}
>
{[10, 20, 30, 40, 50].map((pageSize) => (
<option key={pageSize} value={pageSize}>
Show {pageSize}
</option>
))}
</select>
</div>
</div>
);
};
The generated code implements a handful of features, including data fetching, button actions, pagination, and JSX markup with minimal styles for presenting the data in a table. This is pretty much the skeleton of what we want in a table of data that we want to improve with daisyUI.
It uses the useTable() hook provided by @refinedev/react-table package, which augments Refine's useTable() core hook with React Table's useReactTable() hook. More on this below.
We want to keep most of it and add filter functionality at the top, modify the pagination and apply daisyUI classes for tables, buttons, and groups.
So, we'll build on top of it and make necessary logic, markup and style modifications. Replacing the old ones, we'll eventually adopt the following <ProductList /> code:
Show ProductList component code
import React, { useRef } from "react";
import {
IResourceComponentsProps,
getDefaultFilter,
useDelete,
useNavigation,
} from "@refinedev/core";
import { useTable } from "@refinedev/react-table";
import { ColumnDef, flexRender } from "@tanstack/react-table";
import { PlusIcon } from "@heroicons/react/20/solid";
import {
FunnelIcon,
PencilSquareIcon,
EyeIcon,
TrashIcon,
BarsArrowDownIcon,
BarsArrowUpIcon,
} from "@heroicons/react/24/outline";
export const ProductList: React.FC<IResourceComponentsProps> = () => {
const filterForm: any = useRef(null);
const { mutate: deleteProduct } = useDelete();
const columns = React.useMemo<ColumnDef<any>[]>(
() => [
{
id: "id",
accessorKey: "id",
header: "Id",
},
{
id: "name",
accessorKey: "name",
header: "Name",
},
{
id: "price",
accessorKey: "price",
header: "Price",
},
{
id: "category",
header: "Category",
enableSorting: false,
accessorKey: "category.title",
},
{
id: "description",
accessorKey: "description",
enableSorting: false,
header: "Description",
},
{
id: "actions",
accessorKey: "id",
header: "Actions",
enableSorting: false,
cell: function render({ getValue }) {
return (
<div className="flex justify-around items-center">
<button
className="btn btn-xs btn-circle btn-ghost m-1"
onClick={() => {
edit("products", getValue() as string);
}}
>
<PencilSquareIcon className="h-4 w-4" />
</button>
<button
className="btn btn-xs btn-circle btn-ghost m-1"
onClick={() => {
show("products", getValue() as string);
}}
>
<EyeIcon className="h-4 w-4" />
</button>
<button
className="btn btn-xs btn-circle btn-ghost m-1"
onClick={() => {
deleteProduct({
resource: "products",
id: getValue() as string,
});
}}
>
<TrashIcon className="h-4 w-4 text-error" />
</button>
</div>
);
},
},
],
[],
);
const { edit, show, create } = useNavigation();
const {
getHeaderGroups,
getRowModel,
refineCore: { filters, setCurrent, setFilters },
getState,
setPageIndex,
getCanPreviousPage,
getPageCount,
getCanNextPage,
nextPage,
previousPage,
setPageSize,
} = useTable({
columns,
});
return (
<div className="page-container">
<div className="page-header">
<h1 className="page-title">Products</h1>
<button
className="btn btn-sm btn-primary normal-case font-normal text-zinc-50"
onClick={() => create("products")}
>
<PlusIcon className="h-5 w-5" />
Create
</button>
</div>
<div className="overflow-x-auto bg-slate-50 border">
<div className="flex justify-between items-center m-4">
<button
className="btn btn-outline btn-primary btn-sm normal-case font-light"
onClick={() => {
setCurrent(1);
setFilters([], "replace");
filterForm?.current?.reset();
}}
>
<FunnelIcon className="h-4 w-4" />
Clear
</button>
<div className="flex justify-end items-center">
<form ref={filterForm}>
<input
className="input input-bordered input-sm"
type="search"
value={getDefaultFilter("q", filters)}
onChange={(e) => {
setCurrent(1);
setFilters([
{
field: "q",
value: e.target.value,
operator: "contains",
},
]);
}}
placeholder="Search with keywords"
/>
</form>
</div>
</div>
<table className="table table-zebra border-t">
<thead className="bg-slate-200">
{getHeaderGroups()?.map((headerGroup) => (
<tr key={headerGroup?.id}>
{headerGroup?.headers?.map((header) => (
<th
className="text-center hover:bg-slate-300"
key={header?.id}
onClick={header?.column?.getToggleSortingHandler()}
>
<div className="flex justify-start items-center">
{!header?.isPlaceholder &&
flexRender(
header?.column?.columnDef?.header,
header?.getContext(),
)}
{{
asc: <BarsArrowUpIcon className="h-4 w-4" />,
desc: <BarsArrowDownIcon className="h-4 w-4" />,
}[header?.column?.getIsSorted() as string] ?? null}
</div>
</th>
))}
</tr>
))}
</thead>
<tbody>
{getRowModel()?.rows?.map((row) => (
<tr key={row?.id}>
{row?.getVisibleCells()?.map((cell) => (
<td key={cell?.id}>
{flexRender(
cell?.column?.columnDef?.cell,
cell?.getContext(),
)}
</td>
))}
</tr>
))}
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
<div className="flex justify-center items-center mt-3">
<div className="join">
<button
className="join-item btn btn-sm btn-ghost"
onClick={() => setPageIndex(0)}
disabled={!getCanPreviousPage()}
>
{"<<"}
</button>
<button
className="join-item btn btn-sm btn-ghost"
onClick={() => previousPage()}
disabled={!getCanPreviousPage()}
>
{"<"}
</button>
{Array.from({ length: getPageCount() }, (_, index) => index + 1)?.map(
(pageNumber) => {
const btnActive =
pageNumber - 1 == getState()?.pagination?.pageIndex
? " btn-active"
: "";
return (
<button
key={pageNumber}
className={"join-item btn btn-sm" + btnActive}
onClick={() => setPageIndex(pageNumber - 1)}
>
{pageNumber}
</button>
);
},
)}
<button
className="join-item btn btn-sm btn-ghost"
onClick={() => nextPage()}
disabled={!getCanNextPage()}
>
{">"}
</button>
<button
className="join-item btn btn-sm btn-ghost"
onClick={() => setPageIndex(getPageCount() - 1)}
disabled={!getCanNextPage()}
>
{">>"}
</button>
</div>
<select
className="mx-2 p-1 border rounded"
value={getState()?.pagination?.pageSize}
onChange={(e) => {
setPageSize(Number(e.target.value));
}}
>
{[10, 25, 50].map((pageSize) => (
<option className="border rounded" key={pageSize} value={pageSize}>
{pageSize}
</option>
))}
</select>
</div>
</div>
);
};
It is definitely possible to refactor the components into smaller, testable ones. However, for the purpose of the tutorial, we'll try to keep things on the same page as much as possible. As done below, this will give us the scope to rather focus on explaining the code easily, part by part.
1. Data Fetching and Processing
The useTable() hook from the @refinedev/react-table package is used to fetch data from the Fine Foods /products endpoint. The refine-React Table's useTable() hook is a higher level hook built on top of Refine's core useTable() hook provided by @refinedev/core. It combines the power of useTable() core hook with React Table's useReactTable() APIs:
// Inside ProductList component
const {
getHeaderGroups,
getRowModel,
setOptions,
refineCore: { filters, setCurrent, setFilters },
getState,
setPageIndex,
getCanPreviousPage,
getPageCount,
getCanNextPage,
nextPage,
previousPage,
setPageSize,
} = useTable({
columns,
});
Notice that we are passing React Table column definitions, the columns object, to useTable() hook and grabbing all necessary table props. We are destructuring the table related data with the getRowModel and getHeaderGroups methods and presenting them inside the table.
We are making use of pagination props such as setPageIndex, getPageCount, and previousPage returned by useReactTable() to build the client side pagination strip.
Filtering utilities such as filters, setCurrent, setFilters are accessed from the refineCore object returned from the query. Inside the JSX, we are using them to build the filter by keywords feature.
Notice, we don't need to specify the resource argument to useTable(). It is already inferred from the current URL thanks to the resource and routes definitions in App.tsx.
2. Data Presentation
In the table, we are populating the column headers by looping through the getHeaderGroups() array and presenting row data inside the table by doing the same with the array returned from getRowModel().rows.
Inside the React Table columns definition object, using the cell property we are customizing the contents of the Actions column to add show, edit and delete buttons:
{
id: "actions",
accessorKey: "id",
header: "Actions",
cell: function render({ getValue }) {
return (
<div className="flex justify-around items-center">
<button
className="btn btn-xs btn-circle btn-ghost m-1"
onClick={() => {
edit("products", getValue() as string);
}}
>
<EditIcon />
</button>
<button
className="btn btn-xs btn-circle btn-ghost m-1"
onClick={() => {
show("products", getValue() as string);
}}
>
<ShowIcon />
</button>
<button
className="btn btn-xs btn-circle btn-ghost m-1"
onClick={() => {
deleteProduct({
resource: "products",
id: getValue() as string,
});
}}
>
<DeleteIcon />
</button>
</div>
);
},
},
Notice also, we are using the useNavigation() core hook to pick the show() and edit() methods and use them inside the buttons to navigate to their respective routes:
const { edit, show, create } = useNavigation();
Near the top, we're using the create() method inside the Create button that leads to the <ProductCreate /> page.
3. daisyUI Styles
Throughout the component, we are using short daisyUI classes that come in handy for styling our components. We are using btn and its derived classes such as btn-sm, btn-primary, btn-ghost, btn-circle and btn-outline to style our buttons. For the table, we are using table and table-zebra. For grouping elements, we are using join and join-items.
Notice throughout the markup that we are able to seamlessly apply regular Tailwind Flex, responsive and spacing classes as well. We can also use them to customize the styles of the elements that are already using the component classes.
With these changes, when we navigate to the /products route, our products list page looks like below:
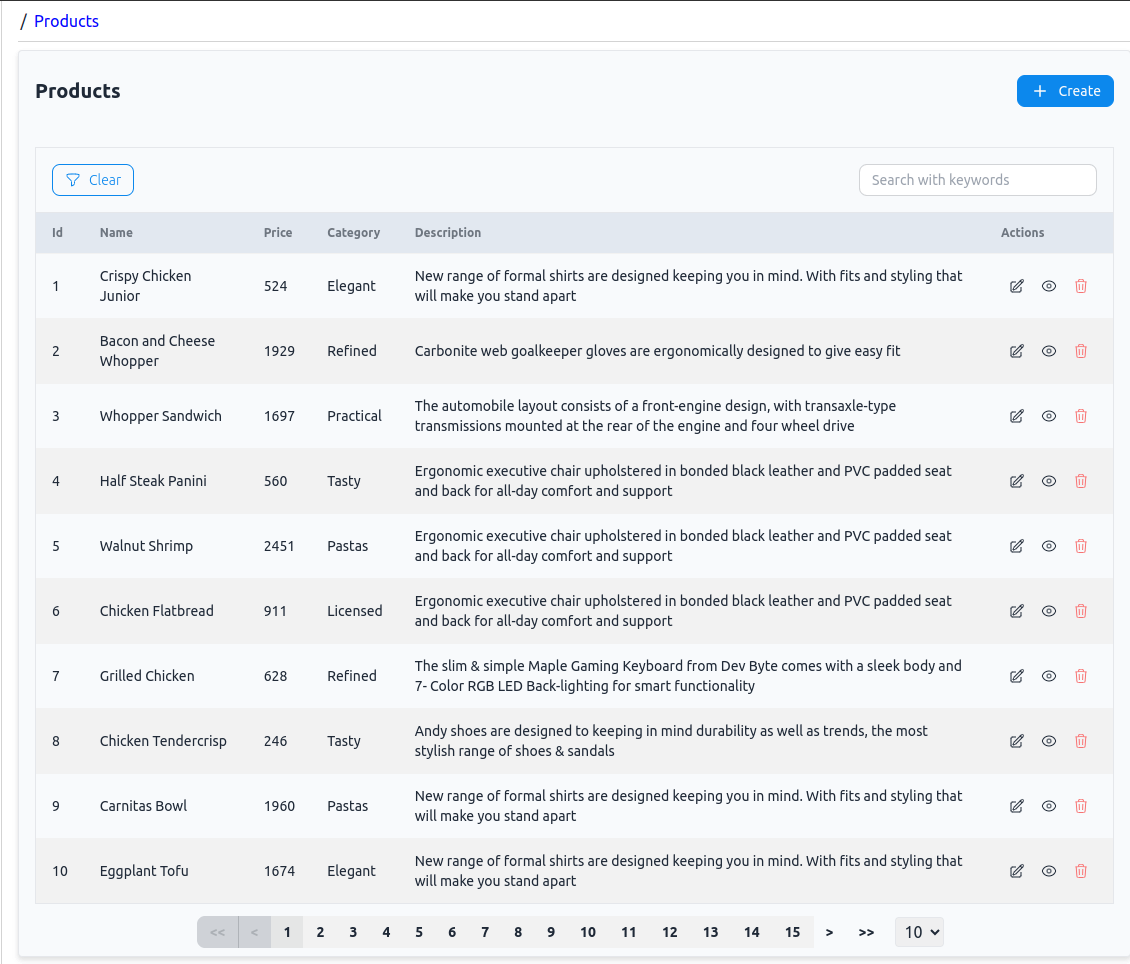
<ProductCreate /> Page
We have already scaffolded the <ProductCreate /> component using the Inferencer. Following the same process described for <ProductList />, we can get the code for <ProductCreate /> component from the page at /products/create. We won't get into the detailed steps here, as moving ahead, you can repeat the process of getting the page code from the modal at all action routes. You can then make the necessary adjustments and come up with the final code.
The <HeadlessInferencer /> uses Refine's @refinedev/react-hook-form APIs to build forms for create and edit pages. The refine-React Hook Form package integrates the useForm() core hook with the features of React Hook Form's useForm() hook.
The modified <ProductCreate /> component looks like below, so replace the code inside src/pages/products/create.tsx with this one:
Show ProductCreate component code
import React from "react";
import {
useNavigation,
IResourceComponentsProps,
useSelect,
} from "@refinedev/core";
import { useForm } from "@refinedev/react-hook-form";
import { ArrowLeftIcon } from "@heroicons/react/24/outline";
export const ProductCreate: React.FC<IResourceComponentsProps> = () => {
const { list } = useNavigation();
const {
refineCore: { onFinish },
register,
handleSubmit,
formState: { errors },
} = useForm();
const { options: categoryOptions } = useSelect({
resource: "categories",
});
return (
<div className="page-container">
<div className="flex justify-start items-center">
<div>
<button
className="mr-2 btn btn-primary btn-sm btn-ghost"
onClick={() => {
list("products");
}}
>
<ArrowLeftIcon className="h-5 w-5" />
</button>
</div>
<h1 className="page-title">Create a Product</h1>
</div>
<form className="mx-2" onSubmit={handleSubmit(onFinish)}>
<div className="form-control my-4">
<label className="m-1">Name</label>
<input
className="input input-sm input-bordered"
type="text"
{...register("name", {
required: "This field is required",
})}
/>
<span style={{ color: "red" }}>
{(errors as any)?.name?.message as string}
</span>
</div>
<div className="form-control my-4">
<label className="m-1">Price</label>
<input
className="input input-sm input-bordered"
type="number"
{...register("price", {
required: "This field is required",
valueAsNumber: true,
})}
/>
<span style={{ color: "red" }}>
{(errors as any)?.price?.message as string}
</span>
</div>
<div className="form-control my-4">
<label className="m-1" htmlFor="category">
Category
</label>
<select
className="input input-sm input-bordered"
placeholder="Select category"
{...register("category.id", {
required: "This field is required",
})}
>
{categoryOptions?.map((option) => (
<option value={option.value} key={option.value}>
{option.label}
</option>
))}
</select>
<span style={{ color: "red" }}>
{(errors as any)?.category?.id?.message as string}
</span>
</div>
<div className="form-control my-4">
<label className="m-1">Description</label>
<textarea
className="textarea textarea-bordered"
rows={5}
style={{ verticalAlign: "top" }}
{...register("description", {
required: "This field is required",
})}
/>
<span style={{ color: "red" }}>
{(errors as any)?.description?.message as string}
</span>
</div>
<div className="flex justify-end items-center my-6">
<input
className="btn btn-primary btn-sm normal-case text-xl text-zinc-50 font-normal"
type="submit"
value="Save"
/>
</div>
</form>
</div>
);
};
Here's the break down of the component:
1. Data Fetching and Form Management
The most significant part of the product create page lies in the use of the useForm() hook imported from @refinedev/react-hook-form supplementary package. The refine-React Hook Form useForm() hook combines the power of the useForm() Refine core hook that primarily handles form submission, data fetching, caching, state management and serverside error handling. Integrating react-hook-form augments form features to include better form fields state management and error handling.
const {
refineCore: { onFinish },
register,
handleSubmit,
formState: { errors },
} = useForm();
We are grabbing the onFinish object returned from the Refine core and passing it to React Hook Form's handleSubmit() submission handler which upon submission passes the field values to the dataProvider.create() method under the hood. Notice we are registering the fields with React Hook Form's register() method for controlling the fields and emitting error messages.
Notice that we are not passing any resource name to useForm(). Like useTable(), it is inferred from the current URL.
We are also using the useSelect() core hook to fetch and populate categories items to present inside <select /> fields.
More on the useSelect() hook in the Refine docs here.
2. daisyUI Style
We are using form related daisyUI style classes such as form-control, input, textarea and their variations like input-sm, input-bordered, textarea-bordered, etc.
Inside the App.css file, we are still able to compose smaller class names from longer ones. For example, page-container and page-title are custom composed reusable classes that help reduce some Tailwind spaghetti strings.
With the above <ProductCreate /> page, when we navigate to the /products/create route, we should be presented with a form to create a product:
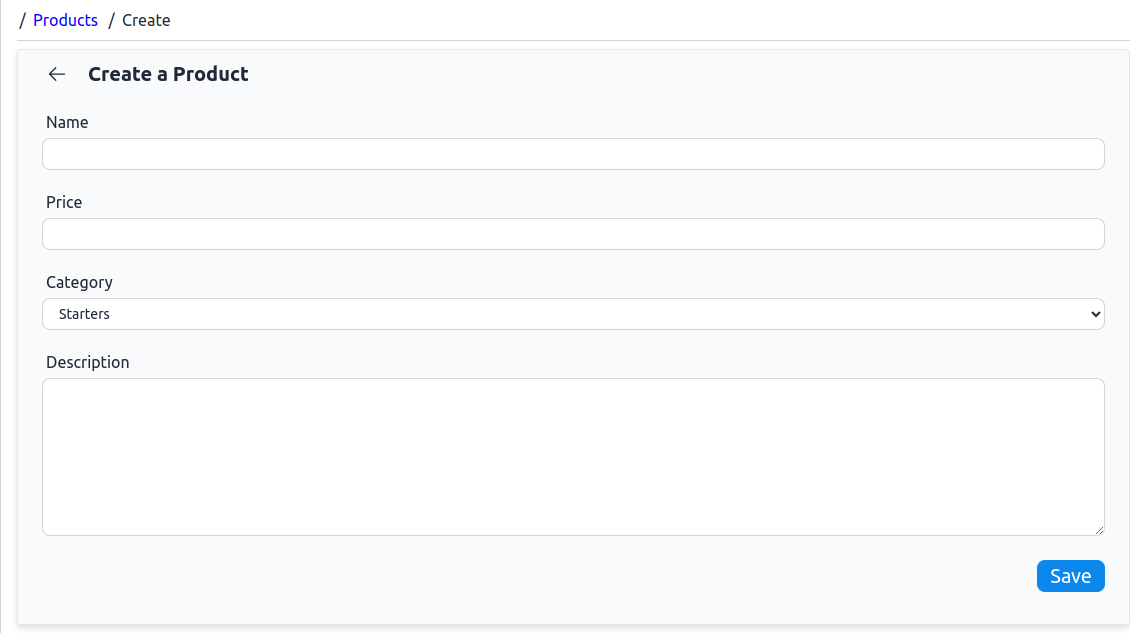
<ProductEdit /> Page
The product edit page will have the same form functionality as the create page. In addition, it will first send a GET request to load the form fields with existing data. The auto-generated <ProductEdit /> page uses the same useForm() refine-React Hook Form hook. We can modify it to implement the above functionalities. So, copy and replace the code in src/pages/products/edit.tsx with this final one:
Show ProductEdit component code
import React from "react";
import {
useNavigation,
IResourceComponentsProps,
useSelect,
} from "@refinedev/core";
import { useForm } from "@refinedev/react-hook-form";
import { ArrowLeftIcon, ArrowPathIcon } from "@heroicons/react/24/outline";
export const ProductEdit: React.FC<IResourceComponentsProps> = () => {
const { list } = useNavigation();
const {
refineCore: { onFinish, queryResult },
register,
handleSubmit,
setValue,
formState: { errors },
} = useForm();
const productsData = queryResult?.data?.data;
const { options: categoryOptions } = useSelect({
resource: "categories",
defaultValue: productsData?.category?.id,
});
React.useEffect(() => {
setValue("category.id", productsData?.category?.id);
}, [productsData, categoryOptions]);
return (
<div className="page-container">
<div className="flex justify-between items-center">
<div className="flex justify-start items-center">
<button
className="mr-2 btn btn-primary btn-sm btn-ghost"
onClick={() => {
list("products");
}}
>
<ArrowLeftIcon className="h-5 w-5" />
</button>
<h1 className="page-title">Edit Product</h1>
</div>
<div>
<button
className="flex justify-center items-center btn btn-sm btn-primary btn-outline normal-case font-normal"
onClick={() => queryResult?.refetch()}
>
<ArrowPathIcon className="h-5 w-5" />
Refresh
</button>
</div>
</div>
<form className="mx-2" onSubmit={handleSubmit(onFinish)}>
<div className="form-control my-4">
<label className="label">Name</label>
<input
className="input input-sm input-bordered"
type="text"
{...register("name", {
required: "This field is required",
})}
/>
<span style={{ color: "red" }}>
{(errors as any)?.name?.message as string}
</span>
</div>
<div className="form-control my-4">
<label className="label">Price</label>
<input
className="input input-sm input-bordered"
type="number"
{...register("price", {
required: "This field is required",
valueAsNumber: true,
})}
/>
<span style={{ color: "red" }}>
{(errors as any)?.price?.message as string}
</span>
</div>
<div className="form-control my-4">
<label className="label">Category</label>
<select
className="input input-sm input-bordered"
placeholder="Select category"
{...register("category.id", {
required: "This field is required",
})}
>
{categoryOptions?.map((option) => (
<option value={option.value} key={option.value}>
{option.label}
</option>
))}
</select>
<span style={{ color: "red" }}>
{(errors as any)?.category?.id?.message as string}
</span>
</div>
<div className="form-control my-4">
<label className="label">Description</label>
<textarea
className="textarea textarea-bordered"
rows={5}
{...register("description", {
required: "This field is required",
})}
/>
<span style={{ color: "red" }}>
{(errors as any)?.description?.message as string}
</span>
</div>
<div className="flex justify-end items-center">
<input
className="btn btn-primary btn-sm normal-case text-xl text-zinc-50 font-normal"
type="submit"
value="Save"
/>
</div>
</form>
</div>
);
};
In the final version of <ProductEdit /> component, we are implementing the same form field control, state management, submission and error handling functionalities as the <ProductCreate /> component implemnted above. We're doing them with the onFinish object, register() and handleSubmit() methods. We are accessing the errors with the formState.errors object. We are also using more or less the same daisyUI classes for buttons and form fields.
Additionally, we are setting the current option of the <select /> dropdown with setValue() method destructured from useForm() hook.
With the <ProductEdit /> component worked out, the page at /product/edit/:id looks like this:
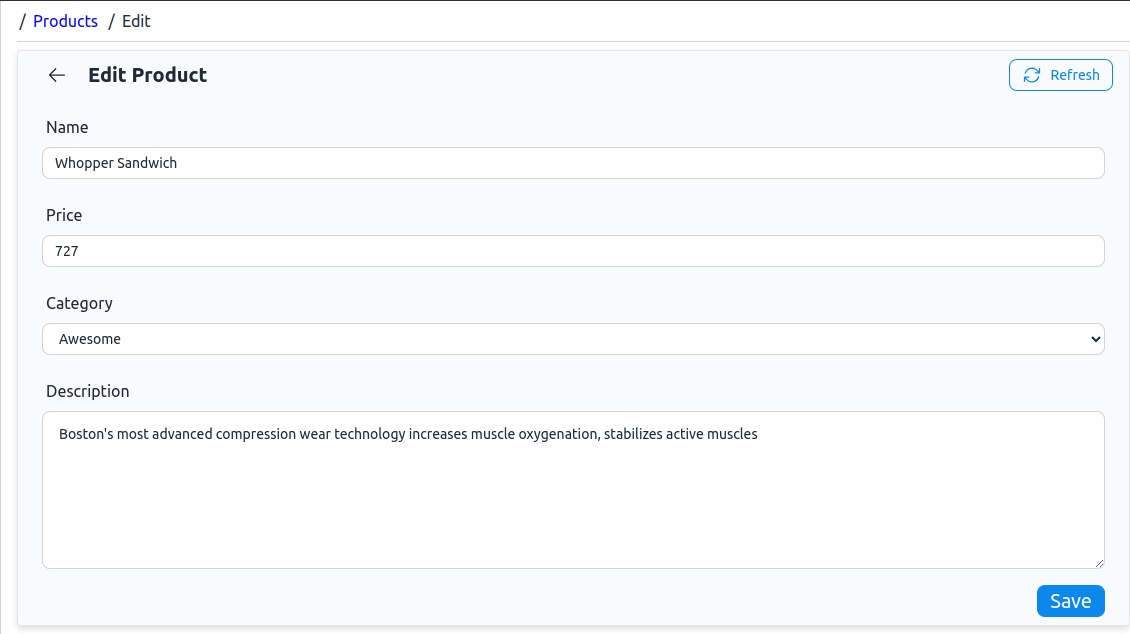
<ProductShow /> Page
The <ProductShow /> component is more straight forward and the final adopted version looks like this:
Show ProductShow component code
import React from "react";
import {
useShow,
useNavigation,
IResourceComponentsProps,
} from "@refinedev/core";
import { ArrowLeftIcon, PencilSquareIcon } from "@heroicons/react/24/outline";
import { IProduct } from "../../interfaces";
export const ProductShow: React.FC<IResourceComponentsProps> = () => {
const { edit, list } = useNavigation();
const {
queryResult: { data },
} = useShow<IProduct>();
const record = data?.data;
const id = record?.id;
return (
<div className="page-container">
<div className="page-header">
<div className="flex justify-start items-center">
<button
className="mr-2 btn btn-primary btn-sm btn-ghost"
onClick={() => list("products")}
>
<ArrowLeftIcon className="h-5 w-5" />
</button>
<h1 className="page-title">Product Details</h1>
</div>
<div className="flex justify-between items-center">
<button
className="flex justify-center items-center btn btn-primary btn-sm text-zinc-50 normal-case font-normal"
onClick={() => edit("products", id ?? "")}
>
<PencilSquareIcon className="h-5 w-5" />
Edit
</button>
</div>
</div>
<div className="card">
<div className="card-body">
<div className="text-xl font-bold">
{record?.name ?? "Loading..."}
</div>
<div className="divider p-0 m-0"></div>
<div className="mb-2">
<h5 className="mb-1 font-bold">Price</h5>
<div>{record?.price ? `$ ${record?.price}` : "Loading..."}</div>
</div>
<div className="mb-2">
<h5 className="mb-1 font-bold">Category</h5>
<div>{record?.category?.title ?? "Loading..."}</div>
</div>
<div className="mb-2">
<h5 className="mb-1 font-bold">Description</h5>
<div>{record?.description ?? "Loading..."}</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
};
In the code above, we are using the useShow() hook and grabbing product details from the queryResult object to display the details in the JSX.
We are also invoking the familiar useNavigation() hook to access the edit() and list() methods and call them from Edit and back buttons respectively.
With the <ProductShow /> page completed, when we navigate to the /products/show/:id path, we can see the product details as below:
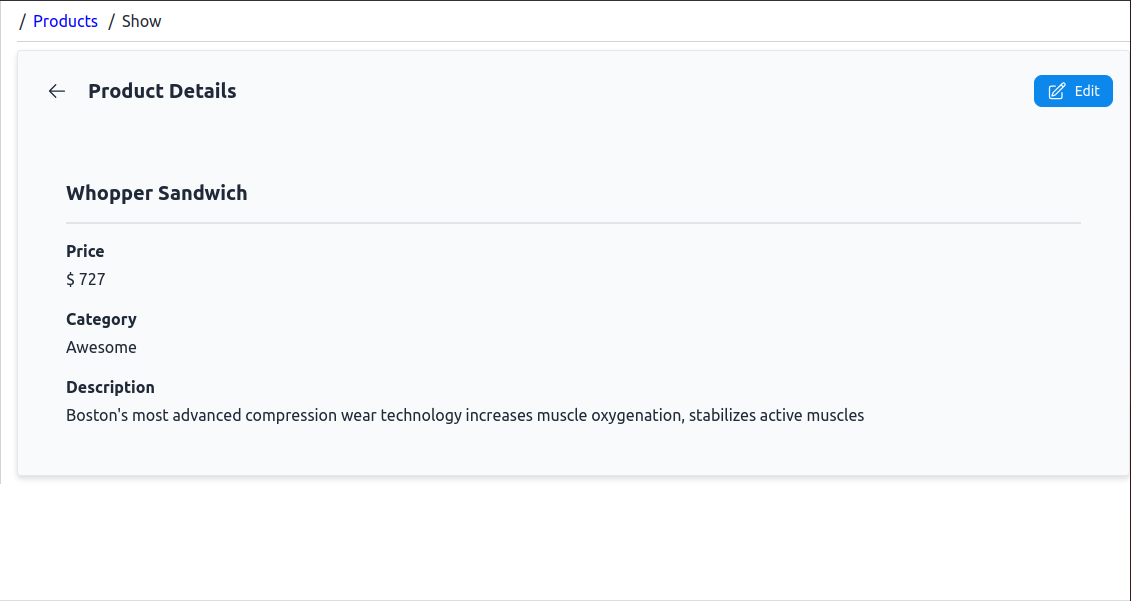
This also means we can navigate back and forth to edit and show pages of a product item from the list page. Or open the create page to create new products.
Category Pages
The category pages are very similar to the product pages. So, I'll quickly add their final versions. You can copy and paste them directly and use them in your files.
Or alternatively, if you want to make your way through generating the code with Inferencers, please feel free to do so.
Run the following Inferencer command anyway to produce the scaffold pages inside the src/pages/categories/ directory:
npm run refine create-resource category
Eventually you'll need to update the resources and routes in App.tsx to this:
src/App.tsx
import { ErrorComponent, GitHubBanner, Refine } from "@refinedev/core";
import { RefineKbar, RefineKbarProvider } from "@refinedev/kbar";
import routerBindings, {
DocumentTitleHandler,
NavigateToResource,
UnsavedChangesNotifier,
} from "@refinedev/react-router-v6";
import dataProvider from "@refinedev/simple-rest";
import {
BrowserRouter,
Navigate,
Outlet,
Route,
Routes,
} from "react-router-dom";
import "./App.css";
import { Layout } from "./components/layout";
import { Dashboard } from "./pages/dashboard";
import {
ProductList,
ProductCreate,
ProductEdit,
ProductShow,
} from "./pages/products";
import {
CategoryList,
CategoryCreate,
CategoryEdit,
CategoryShow,
} from "./pages/categories";
function App() {
return (
<BrowserRouter>
<GitHubBanner />
<RefineKbarProvider>
<Refine
dataProvider={dataProvider("https://api.finefoods.refine.dev")}
routerProvider={routerBindings}
resources={[
{
name: "dashboard",
list: "/dashboard",
},
{
name: "products",
list: "/products",
create: "/products/create",
edit: "/products/edit/:id",
show: "/products/show/:id",
meta: {
canDelete: true,
},
},
{
name: "categories",
list: "/categories",
create: "/categories/create",
edit: "/categories/edit/:id",
show: "/categories/show/:id",
meta: {
canDelete: true,
},
},
]}
options={{
syncWithLocation: true,
warnWhenUnsavedChanges: true,
}}
>
<Routes>
<Route
element={
<Layout>
<Outlet />
</Layout>
}
>
<Route index element={<Navigate to="/dashboard" />} />
<Route path="/dashboard">
<Route index element={<Dashboard />} />
</Route>
<Route path="/products">
<Route index element={<ProductList />} />
<Route path="create" element={<ProductCreate />} />
<Route path="edit/:id" element={<ProductEdit />} />
<Route path="show/:id" element={<ProductShow />} />
</Route>
<Route path="/categories">
<Route index element={<CategoryList />} />
<Route path="create" element={<CategoryCreate />} />
<Route path="edit/:id" element={<CategoryEdit />} />
<Route path="show/:id" element={<CategoryShow />} />
</Route>
<Route path="*" element={<ErrorComponent />} />
</Route>
</Routes>
<RefineKbar />
<UnsavedChangesNotifier />
<DocumentTitleHandler />
</Refine>
</RefineKbarProvider>
</BrowserRouter>
);
}
export default App;
<CategoryList /> Page
For the final version of <CategoryList />, adopt the following code.
Show CategoryList component code
import React, { useRef } from "react";
import {
IResourceComponentsProps,
getDefaultFilter,
useDelete,
useNavigation,
} from "@refinedev/core";
import { useTable } from "@refinedev/react-table";
import { ColumnDef, flexRender } from "@tanstack/react-table";
import { PlusIcon } from "@heroicons/react/20/solid";
import {
FunnelIcon,
PencilSquareIcon,
EyeIcon,
TrashIcon,
BarsArrowDownIcon,
BarsArrowUpIcon,
} from "@heroicons/react/24/outline";
import { ICategory } from "../../interfaces";
export const CategoryList: React.FC<IResourceComponentsProps> = () => {
const filterForm: any = useRef(null);
const { mutate: deleteCategory } = useDelete<ICategory>();
const columns = React.useMemo<ColumnDef<any>[]>(
() => [
{
id: "id",
accessorKey: "id",
header: "Id",
},
{
id: "title",
accessorKey: "title",
header: "Name",
cell: function render({ getValue }) {
return (
<div className="w-24 md:w-60 lg:w-96 text-center">
{getValue() as string}
</div>
);
},
},
{
id: "actions",
accessorKey: "id",
header: "Actions",
enableSorting: false,
cell: function render({ getValue }) {
return (
<div className="flex justify-around items-center">
<button
className="btn btn-xs btn-circle btn-ghost m-1"
onClick={() => {
edit("categories", getValue() as string);
}}
>
<PencilSquareIcon className="h-4 w-4" />
</button>
<button
className="btn btn-xs btn-circle btn-ghost m-1"
onClick={() => {
show("categories", getValue() as string);
}}
>
<EyeIcon className="h-4 w-4" />
</button>
<button
className="btn btn-xs btn-circle btn-ghost m-1"
onClick={() => {
deleteCategory({
resource: "categories",
id: getValue() as string,
});
}}
>
<TrashIcon className="h-4 w-4 text-error" />
</button>
</div>
);
},
},
],
[],
);
const { edit, show, create } = useNavigation();
const {
getHeaderGroups,
getRowModel,
refineCore: { setCurrent, filters, setFilters },
getState,
setPageIndex,
getCanPreviousPage,
getPageCount,
getCanNextPage,
nextPage,
previousPage,
setPageSize,
} = useTable({
columns,
});
return (
<div className="page-container">
<div className="page-header">
<h1 className="page-title">Categories</h1>
<button
className="btn btn-sm btn-primary normal-case font-normal text-zinc-50"
onClick={() => create("categories")}
>
<PlusIcon className="h-5 w-5" />
Create
</button>
</div>
<div className="overflow-x-auto bg-slate-50 border">
<div className="flex justify-between items-center m-4">
<button
className="btn btn-outline btn-primary btn-sm normal-case font-light"
onClick={() => {
setCurrent(1);
setFilters([], "replace");
filterForm?.current?.reset();
}}
>
<FunnelIcon className="h-4 w-4" />
Clear
</button>
<div className="flex justify-end items-center">
<form ref={filterForm}>
<input
className="input input-bordered input-sm"
type="search"
value={getDefaultFilter("q", filters)}
onChange={(e) => {
setCurrent(1);
setFilters([
{
field: "q",
value: e.target.value,
operator: "contains",
},
]);
}}
placeholder="Search with keywords"
/>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<table className="table table-zebra border-t">
<thead className="bg-slate-200">
{getHeaderGroups()?.map((headerGroup) => (
<tr key={headerGroup?.id}>
{headerGroup?.headers?.map((header) => (
<th
className="text-center hover:bg-slate-300"
key={header?.id}
onClick={header?.column?.getToggleSortingHandler()}
>
<div className="flex justify-center items-center">
{!header?.isPlaceholder &&
flexRender(
header?.column?.columnDef?.header,
header?.getContext(),
)}
{{
asc: <BarsArrowUpIcon className="h-4 w-4" />,
desc: <BarsArrowDownIcon className="h-4 w-4" />,
}[header?.column?.getIsSorted() as string] ?? null}
</div>
</th>
))}
</tr>
))}
</thead>
<tbody>
{getRowModel()?.rows?.map((row) => (
<tr key={row?.id}>
{row?.getVisibleCells()?.map((cell) => (
<td className="text-center" key={cell?.id}>
<div className="flex justify-center items-center">
{flexRender(
cell?.column?.columnDef?.cell,
cell?.getContext(),
)}
</div>
</td>
))}
</tr>
))}
</tbody>
</table>
<div className="flex justify-center items-center mt-3">
<div className="join">
<button
className="join-item btn btn-sm btn-ghost"
onClick={() => setPageIndex(0)}
disabled={!getCanPreviousPage()}
>
{"<<"}
</button>
<button
className="join-item btn btn-sm btn-ghost"
onClick={() => previousPage()}
disabled={!getCanPreviousPage()}
>
{"<"}
</button>
{Array.from({ length: getPageCount() }, (_, index) => index + 1)?.map(
(pageNumber) => {
const btnActive =
pageNumber - 1 == getState()?.pagination?.pageIndex
? " btn-active"
: "";
return (
<button
key={pageNumber}
className={"join-item btn btn-sm" + btnActive}
onClick={() => setPageIndex(pageNumber - 1)}
>
{pageNumber}
</button>
);
},
)}
<button
className="join-item btn btn-sm btn-ghost"
onClick={() => nextPage()}
disabled={!getCanNextPage()}
>
{">"}
</button>
<button
className="join-item btn btn-sm btn-ghost"
onClick={() => setPageIndex(getPageCount() - 1)}
disabled={!getCanNextPage()}
>
{">>"}
</button>
</div>
<select
className="mx-2 p-1 border rounded"
value={getState()?.pagination?.pageSize}
onChange={(e) => {
setPageSize(Number(e.target.value));
}}
>
{[10, 25, 50].map((pageSize) => (
<option className="border rounded" key={pageSize} value={pageSize}>
{pageSize}
</option>
))}
</select>
</div>
</div>
);
};
<CategoryCreate /> Page
For the final version of the <CategoryCreate /> component, adopt this code:
Show CategoryCreate component code
import React from "react";
import { useNavigation, IResourceComponentsProps } from "@refinedev/core";
import { useForm } from "@refinedev/react-hook-form";
import { ArrowLeftIcon } from "@heroicons/react/24/outline";
export const CategoryCreate: React.FC<IResourceComponentsProps> = () => {
const { list } = useNavigation();
const {
refineCore: { onFinish },
register,
handleSubmit,
formState: { errors },
} = useForm();
return (
<div className="page-container">
<div className="flex justify-start items-center">
<div>
<button
className="mr-2 btn btn-primary btn-sm btn-ghost"
onClick={() => {
list("categories");
}}
>
<ArrowLeftIcon className="h-4 w-4" />
</button>
</div>
<h1 className="page-title">Create a Category</h1>
</div>
<form className="mx-2" onSubmit={handleSubmit(onFinish)}>
<div className="form-control my-4">
<label className="label">Name</label>
<input
className="input input-sm input-bordered"
type="text"
{...register("title", {
required: "This field is required",
})}
/>
<span style={{ color: "red" }}>
{(errors as any)?.title?.message as string}
</span>
<div className="flex justify-end items-center my-6">
<input
className="btn btn-primary btn-sm normal-case text-xl text-zinc-50 font-normal"
type="submit"
value="Save"
/>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
);
};
<CategoryEdit /> Page
For the final version of the <CategoryEdit /> component, adopt this code:
Show CategoryEdit component code
import React from "react";
import { useNavigation, IResourceComponentsProps } from "@refinedev/core";
import { useForm } from "@refinedev/react-hook-form";
import { ArrowLeftIcon, ArrowPathIcon } from "@heroicons/react/24/outline";
export const CategoryEdit: React.FC<IResourceComponentsProps> = () => {
const { list } = useNavigation();
const {
refineCore: { onFinish, queryResult },
register,
handleSubmit,
formState: { errors },
} = useForm();
return (
<div className="page-container">
<div className="flex justify-between items-center">
<div className="flex justify-start items-center">
<button
className="mr-2 btn btn-primary btn-sm btn-ghost"
onClick={() => {
list("categories");
}}
>
<ArrowLeftIcon className="h-5 w-5" />
</button>
<h1 className="page-title">Edit Category</h1>
</div>
<div>
<button
className="flex justify-center items-center btn btn-sm btn-primary btn-outline normal-case font-normal"
onClick={() => queryResult?.refetch()}
>
<ArrowPathIcon className="h-5 w-5" />
Refresh
</button>
</div>
</div>
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit(onFinish)}>
<div className="form-control my-4">
<label className="label">Name</label>
<input
className="input input-sm input-bordered"
type="text"
{...register("title", {
required: "This field is required",
})}
/>
<span style={{ color: "red" }}>
{(errors as any)?.title?.message as string}
</span>
</div>
<div className="flex justify-end items-center">
<input
className="btn btn-primary btn-sm normal-case text-xl text-zinc-50 font-normal"
type="submit"
value="Save"
/>
</div>
</form>
</div>
);
};
<CategoryShow /> Page
For the final version of the <CategoryShow /> page, adopt this code:
Show CategoryShow component code
import React from "react";
import {
useShow,
useNavigation,
IResourceComponentsProps,
} from "@refinedev/core";
import { ArrowLeftIcon, PencilSquareIcon } from "@heroicons/react/24/outline";
import { ICategory } from "../../interfaces";
export const CategoryShow: React.FC<IResourceComponentsProps> = () => {
const { edit, list } = useNavigation();
const {
queryResult: { data },
} = useShow<ICategory>();
const record = data?.data;
return (
<div className="page-container">
<div className="page-header">
<div className="flex justify-between items-center">
<button
className="mr-2 btn btn-primary btn-sm btn-ghost"
onClick={() => list("categories")}
>
<ArrowLeftIcon className="h-5 w-5" />
</button>
<h1 className="page-title">Category Details</h1>
</div>
<div className="flex justify-start items-center">
<button
className="flex justify-center items-center btn btn-primary btn-sm text-zinc-50 normal-case font-normal"
onClick={() => edit("categories", record?.id ?? "")}
>
<PencilSquareIcon className="h-5 w-5" />
Edit
</button>
</div>
</div>
<div className="card">
<div className="card-body">
<div className="mb-2">
<h5 className="text-xl font-bold">Id</h5>
<div>{record?.id ?? "Loading..."}</div>
</div>
<div className="mb-2">
<h5 className="text-xl font-bold">Name</h5>
<div>{record?.title ?? "Loading..."}</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
};
After all these changes for the category resource, we should be able to navigate across the category pages as below:
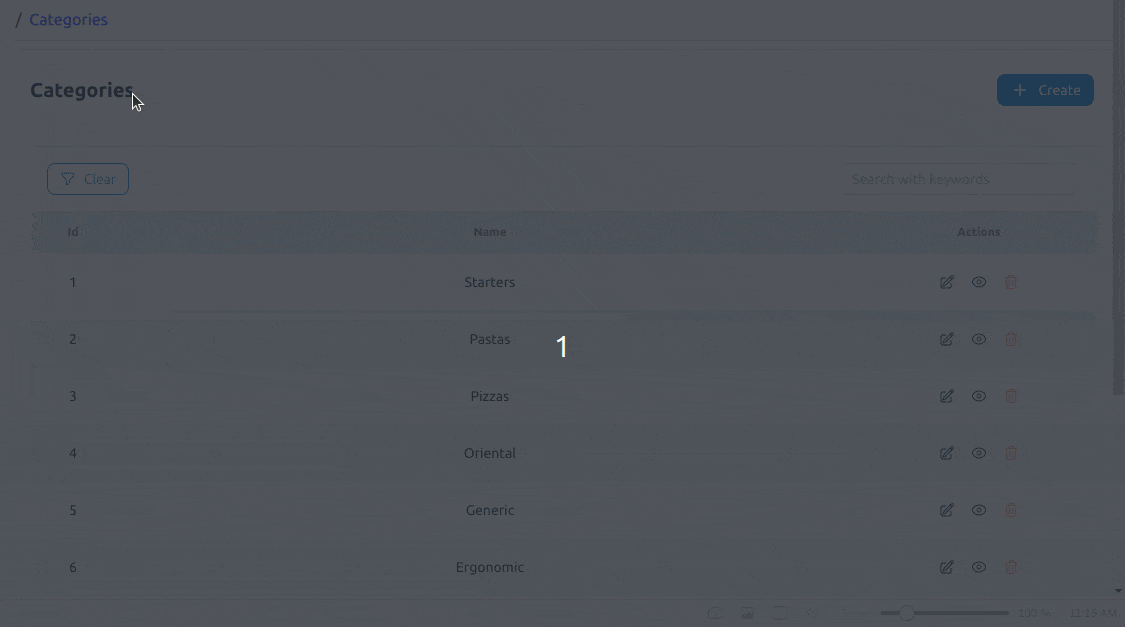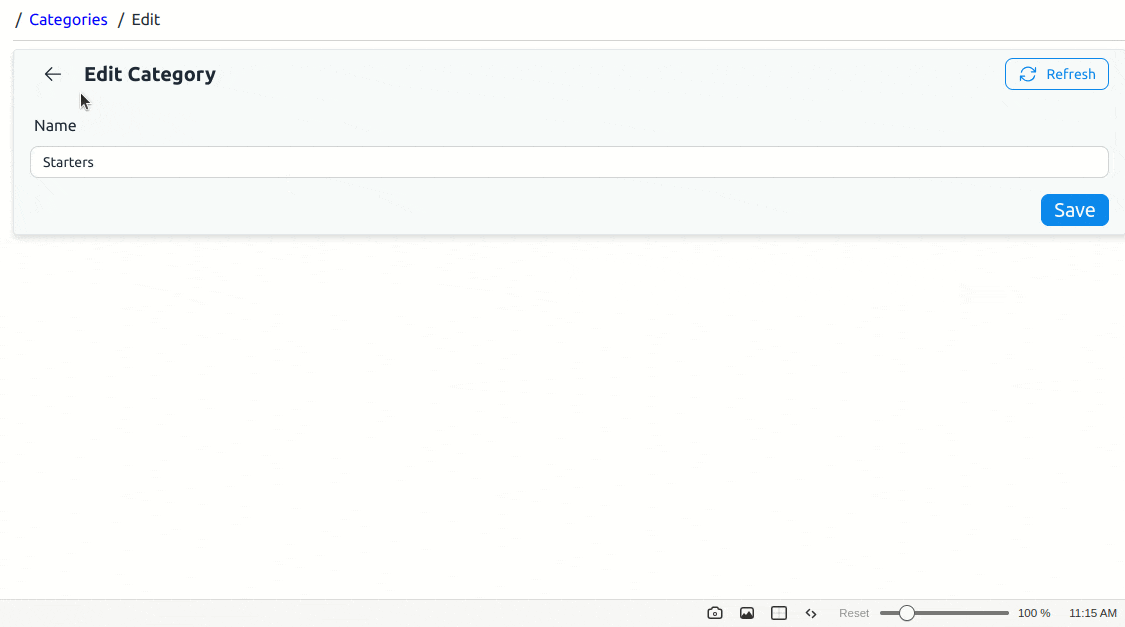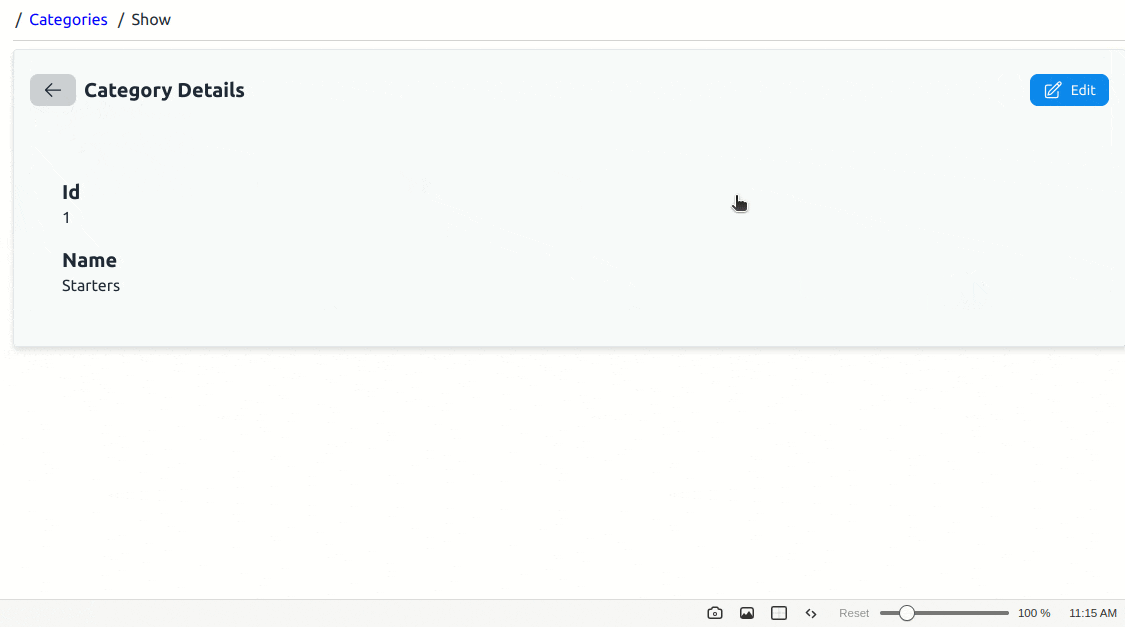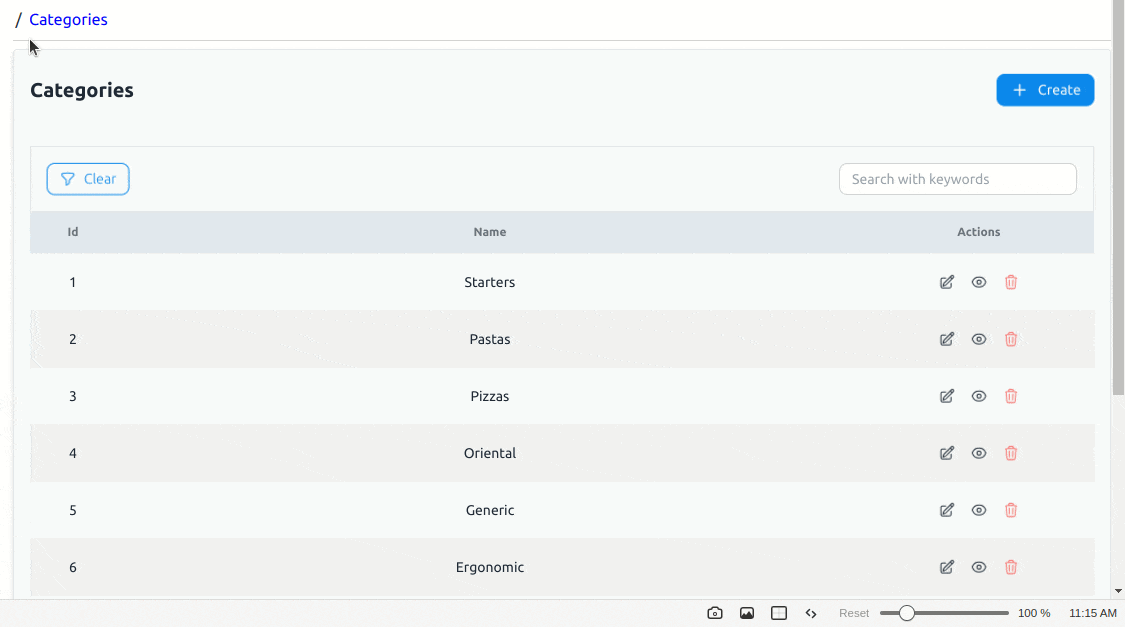
Update the Layout
In this section, we'll customize the app layout for a top navbar menu with icons for each item. In Refine, the <Layout /> component is passed to the topmost <Route /> element, meaning it becomes a common partial to all pages:
<Refine>
<Routes>
<Route
element={
<Layout>
<Outlet />
</Layout>
}
>
<Route path="*" element={<ErrorComponent />} />
</Route>
</Routes>
</Refine>
The Layout Component
Currently, the layout places the navigation menu to the left of the page. We want to move it to the top as a navbar.
To begin with, we'll remove Refine's layout class from there and add some Tailwind classes to move the items to the top. At src/components/layout/index.tsx, make it look like this:
import { PropsWithChildren } from "react";
import { Breadcrumb } from "../breadcrumb";
import { Menu } from "../menu";
export const Layout: React.FC<PropsWithChildren> = ({ children }) => {
return (
<div>
<Menu />
<div className="p-4 bg-zinc-100">
<Breadcrumb />
<div>{children}</div>
</div>
</div>
);
};
Notice it renders the <Menu /> and <Breadcrumb /> components. We'll update them too, but we'll first add icons to each resource in the resources definition in App.tsx. Update the resources array with icons and necessary imports:
src/App.tsx
import { ErrorComponent, GitHubBanner, Refine } from "@refinedev/core";
import { RefineKbar, RefineKbarProvider } from "@refinedev/kbar";
import routerBindings, {
DocumentTitleHandler,
UnsavedChangesNotifier,
} from "@refinedev/react-router-v6";
import dataProvider from "@refinedev/simple-rest";
import {
BrowserRouter,
Navigate,
Outlet,
Route,
Routes,
} from "react-router-dom";
import "./App.css";
import { Layout } from "./components/layout";
import {
ProductCreate,
ProductEdit,
ProductList,
ProductShow,
} from "./pages/products";
import {
CategoryCreate,
CategoryEdit,
CategoryList,
CategoryShow,
} from "./pages/categories";
import { Dashboard } from "./pages/dashboard";
import { HomeIcon, ShoppingCartIcon, TagIcon } from "@heroicons/react/20/solid";
function App() {
return (
<BrowserRouter>
<GitHubBanner />
<RefineKbarProvider>
<Refine
dataProvider={dataProvider("https://api.finefoods.refine.dev")}
routerProvider={routerBindings}
resources={[
{
name: "dashboard",
list: "/dashboard",
meta: {
icon: <HomeIcon className="h-4 w-4" />,
},
},
{
name: "products",
list: "/products",
create: "/products/create",
edit: "/products/edit/:id",
show: "/products/show/:id",
meta: {
icon: <ShoppingCartIcon className="h-4 w-4" />,
canDelete: true,
},
},
{
name: "categories",
list: "/categories",
create: "/categories/create",
edit: "/categories/edit/:id",
show: "/categories/show/:id",
meta: {
icon: <TagIcon className="h-4 w-4" />,
canDelete: true,
},
},
]}
options={{
syncWithLocation: true,
warnWhenUnsavedChanges: true,
}}
>
<Routes>
<Route
element={
<Layout>
<Outlet />
</Layout>
}
>
<Route index element={<Navigate to="/dashboard" />} />
<Route path="/dashboard">
<Route index element={<Dashboard />} />
</Route>
<Route path="/products">
<Route index element={<ProductList />} />
<Route path="create" element={<ProductCreate />} />
<Route path="edit/:id" element={<ProductEdit />} />
<Route path="show/:id" element={<ProductShow />} />
</Route>
<Route path="/categories">
<Route index element={<CategoryList />} />
<Route path="create" element={<CategoryCreate />} />
<Route path="edit/:id" element={<CategoryEdit />} />
<Route path="show/:id" element={<CategoryShow />} />
</Route>
<Route path="*" element={<ErrorComponent />} />
</Route>
</Routes>
<RefineKbar />
<UnsavedChangesNotifier />
<DocumentTitleHandler />
</Refine>
</RefineKbarProvider>
</BrowserRouter>
);
}
export default App;
Adding icons to resources makes them available for menu items as well as breadcrumbs. So, now we'll update the <Menu /> and <Breadcrumb /> components with icons and daisyUI styles.
Menu Component
Change the <Menu /> component to the below code:
src/components/menu/index.tsx
import { useMenu } from "@refinedev/core";
import { NavLink } from "react-router-dom";
export const Menu = () => {
const { menuItems } = useMenu();
return (
<nav className="sticky top-0 z-50 menu mx-0 bg-white">
<ul className="mx-0 flex justify-start items-center">
{menuItems.map((item) => (
<li key={item?.key} className="mx-0 flex justify-start items-center">
<div className="text-gray-600">
<NavLink
className="text-lg flex items-center"
to={item?.route ?? "/"}
>
<span className="mr-2">{item?.icon}</span>
{item?.label}
</NavLink>
</div>
</li>
))}
</ul>
</nav>
);
};
Notice now that we are displaying an icon beside each menu item and we are also using the daisyUI menu class to style the menu.
Breadcrumb Component
Then update <Breadcrumb /> component to look like below:
src/components/breadcrumb/index.tsx
import { useBreadcrumb } from "@refinedev/core";
import { Link } from "react-router-dom";
export const Breadcrumb = () => {
const { breadcrumbs } = useBreadcrumb();
if (breadcrumbs.length == 1) return null;
return (
<div className="text-sm breadcrumbs">
<ul className="my-2">
{breadcrumbs?.map((breadcrumb) => {
return (
<li key={`breadcrumb-${breadcrumb?.label}`}>
<span className="mx-2">{breadcrumb?.icon}</span>
{breadcrumb?.href ? (
<Link to={breadcrumb?.href}>{breadcrumb?.label}</Link>
) : (
<span>{breadcrumb?.label}</span>
)}
</li>
);
})}
</ul>
</div>
);
};
Notice also that we are displaying the icons beside the resource name in each breadcrumb. We are using the daisyUI breadcrumbs class to style the elements.
With these changes, we should now see a sticky top navbar with items that give access to all the resource list pages. Also, breadcrumbs should show up along a resource path:
Here's the walkthrough of all the resource list pages:
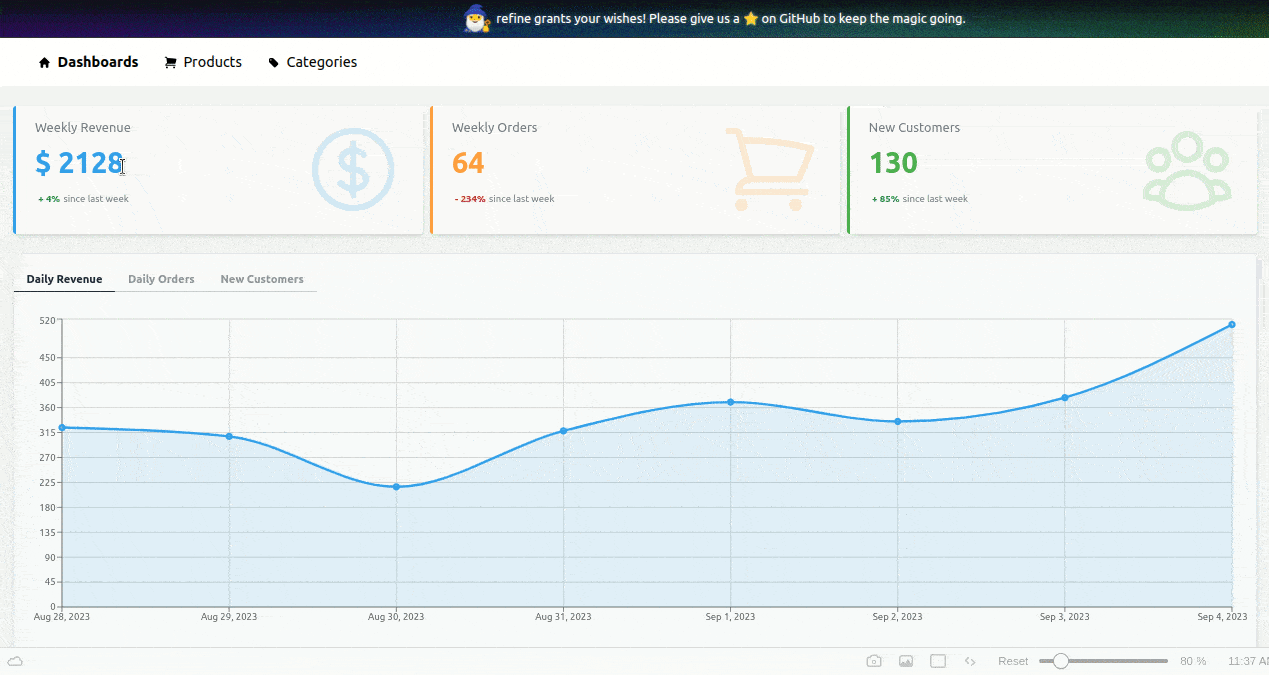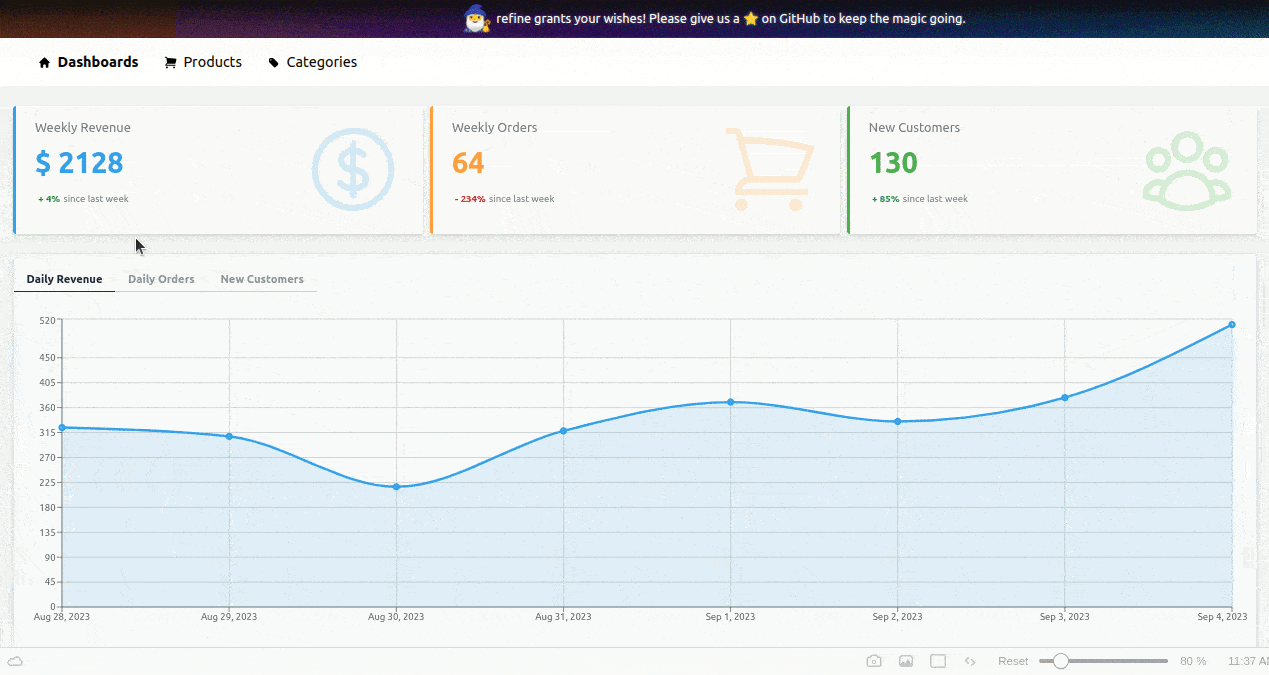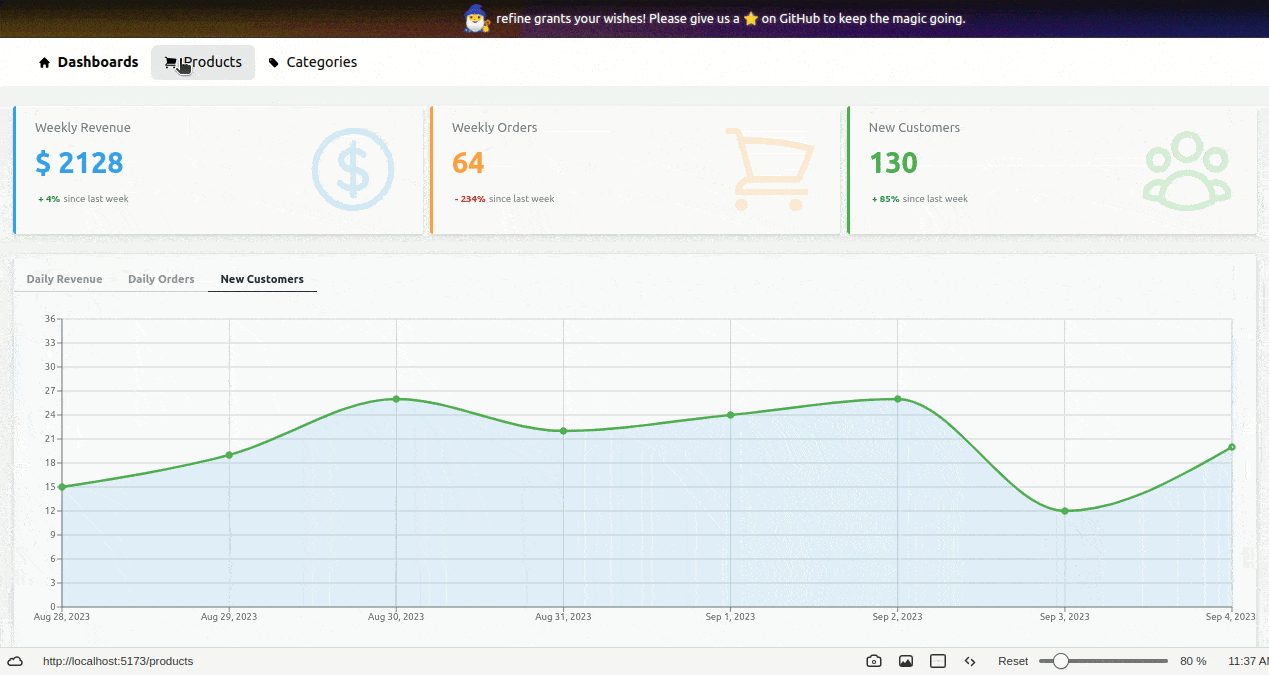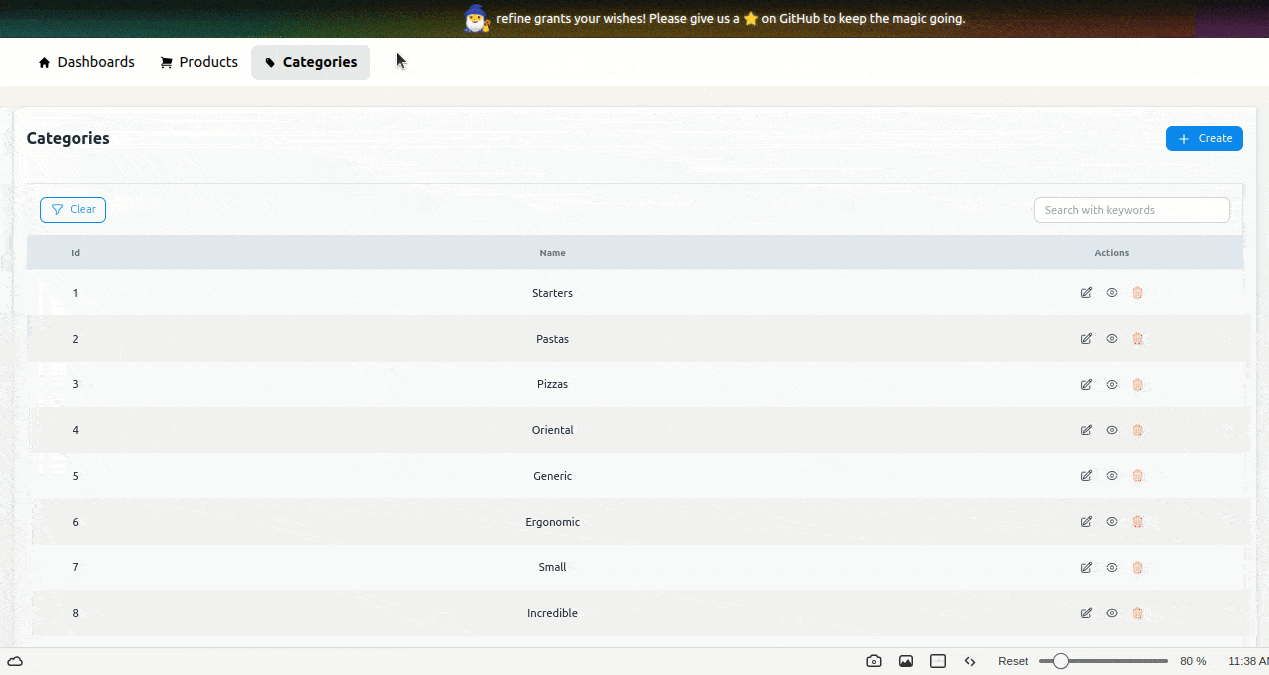
Summary
In this post, we got familiar with how to build a React dashboard and admin panel with Refine and daisyUI. We saw how to easily integrate daisyUI with Refine's headless core and supplementary packages for React Table and React Hook Form.
We used the Fine Foods API for our app. We first built a dashboard page to present several KPI data in cards, charts and a table. While doing so, we learned how to use Refine's core useList() hook, and its excellent support for presenting data in tables with useTable() by integrating with React Table. We used Recharts plotting library to create charts of our KPI data. We utilized daisyUI templates with prestyled component classes to style the cards and table.
We generated CRUD pages with the Inferencer tool, and we went ahead to further customize them according to our needs. We styled them conveniently with short, semantic, component ready classes offered by daisyUI. We also felt the need to use regular Tailwind Flex, color, size, shape and responsive utility classes, and found that daisyUI offers such flexibility out-of-the-box.
We saw that Refine brings the power of React Hook Form into its pages with its supplementary @refinedev/react-form-hook package that helps effortlessly manage data fetching, form state, caching and error handling in a CRUD application with the useForm() hook. We found that daisyUI can fit in seamlessly among all to build enterprise level data-heavy applications like admin panels, dashboards and other internal tools.
We initially dashed, frequently dazed, and finally established an admin panel by getting refine.d.
Live CodeSandbox Example
npm create refine-app@latest -- --example blog-refine-daisyui

